Genome sequencing of a Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolate of a successful international clone with decreased susceptibility and resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporins
- PMID: 22908152
- PMCID: PMC3486552
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00636-12
Genome sequencing of a Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolate of a successful international clone with decreased susceptibility and resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporins
Abstract
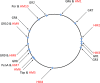
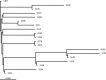
The recent emergence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains with decreased susceptibility to extended-spectrum cephalosporins is a major concern globally. We sequenced the genome of an N. gonorrhoeae multiantigen sequence typing (NG-MAST) ST1407 isolate (SM-3) with decreased susceptibility and resistance to oral extended-spectrum cephalosporins. The isolate was cultured in 2008 in San Francisco, CA, and possessed mosaic penA allele XXXIV, which is associated with an international clone that possesses decreased susceptibility as well as resistance to oral extended-spectrum cephalosporins globally. The genome sequence of strain NCCP11945 was used as a scaffold, and our assembly resulted in 91 contigs covering 2,029,064 bp (91%; >150× coverage) of the genome. Numerous instances of suspected horizontal genetic transfer events with other Neisseria species were identified, and two genes, opa and txf, acquired from nongonococcal Neisseria species, were identified. Strains possessing mosaic penA alleles (n = 108) and nonmosaic penA alleles (n = 169) from the United States and Europe (15 countries), cultured in 2002 to 2009, were screened for the presence of these genes. The opa gene was detected in most (82%) penA mosaic-containing isolates (mainly from 2007 to 2009) but not in any penA nonmosaic isolates. The txf gene was found in all strains containing opa but also in several (18%) penA nonmosaic strains. Using opa and txf as genetic markers, we identified a strain that possesses mosaic penA allele XXXIV, but the majority of its genome is not genetically related to strain SM-3. This implies that penA mosaic allele XXXIV was transferred horizontally. Such isolates also possessed decreased susceptibility and resistance to oral extended-spectrum cephalosporins. These findings support that genetic screening for particular penA mosaic alleles can be a valuable method for tracking strains with decreased susceptibility as well as resistance to oral extended-spectrum cephalosporins worldwide and that screening using only NG-MAST may not be sufficient.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

