Glycosylation is dispensable for sorting of synaptotagmin 1 but is critical for targeting of SV2 and synaptophysin to recycling synaptic vesicles
- PMID: 22908222
- PMCID: PMC3471705
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.398883
Glycosylation is dispensable for sorting of synaptotagmin 1 but is critical for targeting of SV2 and synaptophysin to recycling synaptic vesicles
Abstract
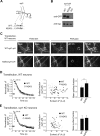
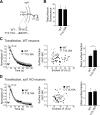
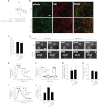
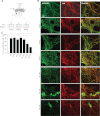
Glycosylation is a major form of post-translational modification of synaptic vesicle membrane proteins. For example, the three major synaptic vesicle glycoproteins, synaptotagmin 1, synaptophysin, and SV2, represent ∼30% of the total copy number of vesicle proteins. Previous studies suggested that glycosylation is required for the vesicular targeting of synaptotagmin 1, but the role of glycosylation of synaptophysin and SV2 has not been explored in detail. In this study, we analyzed all glycosylation sites on synaptotagmin 1, synaptophysin, and SV2A via mutagenesis and optical imaging of pHluorin-tagged proteins in cultured neurons from knock-out mice lacking each protein. Surprisingly, these experiments revealed that glycosylation is completely dispensable for the sorting of synaptotagmin 1 to SVs whereas the N-glycans on SV2A are only partially dispensable. In contrast, N-glycan addition is essential for the synaptic localization and function of synaptophysin. Thus, glycosylation plays distinct roles in the trafficking of each of the three major synaptic vesicle glycoproteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cotrafficking of SV2 and synaptotagmin at the synapse.J Neurosci. 2010 Apr 21;30(16):5569-78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4781-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20410110 Free PMC article.
-
The synaptic vesicle proteins SV2, synaptotagmin and synaptophysin are sorted to separate cellular compartments in CHO fibroblasts.J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(3):575-84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.3.575. J Cell Biol. 1993. PMID: 7901222 Free PMC article.
-
SV2A controls the surface nanoclustering and endocytic recruitment of Syt1 during synaptic vesicle recycling.J Neurochem. 2024 Sep;168(9):3188-3208. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16186. Epub 2024 Aug 1. J Neurochem. 2024. PMID: 39091022
-
Synaptic vesicle proteins and regulated exocytosis.J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:75-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.11. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993. PMID: 8144706 Review.
-
Control of Synaptotagmin-1 Trafficking by SV2A-Mechanism and Consequences for Presynaptic Function and Dysfunction.J Neurochem. 2025 Jan;169(1):e16308. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16308. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 39853744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptic vesicle pool-specific modification of neurotransmitter release by intravesicular free radical generation.J Physiol. 2017 Feb 15;595(4):1223-1238. doi: 10.1113/JP273115. Epub 2016 Dec 2. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27723113 Free PMC article.
-
The role of protein N-glycosylation in neural transmission.Glycobiology. 2014 May;24(5):407-17. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwu015. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Glycobiology. 2014. PMID: 24643084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptic dysfunction induced by glycine-alanine dipeptides in C9orf72-ALS/FTD is rescued by SV2 replenishment.EMBO Mol Med. 2020 May 8;12(5):e10722. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201910722. Epub 2020 Apr 29. EMBO Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32347002 Free PMC article.
-
Gangliosides interact with synaptotagmin to form the high-affinity receptor complex for botulinum neurotoxin B.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Sep 3;116(36):18098-18108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1908051116. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31431523 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic vesicle protein 2: A multi-faceted regulator of secretion.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Nov;95:130-141. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.02.003. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30826548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonanomi D., Benfenati F., Valtorta F. (2006) Protein sorting in the synaptic vesicle life cycle. Prog. Neurobiol. 80, 177–217 - PubMed
-
- Hannah M. J., Schmidt A. A., Huttner W. B. (1999) Synaptic vesicle biogenesis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 15, 733–798 - PubMed
-
- Sampo B., Kaech S., Kunz S., Banker G. (2003) Two distinct mechanisms target membrane proteins to the axonal surface. Neuron 37, 611–624 - PubMed
-
- Kittler J. T., Moss S. J. (2003) Modulation of GABAA receptor activity by phosphorylation and receptor trafficking: implications for the efficacy of synaptic inhibition. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 13, 341–347 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

