Serine 123 phosphorylation modulates p21 protein stability and activity by suppressing ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation
- PMID: 22908227
- PMCID: PMC3464546
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.384990
Serine 123 phosphorylation modulates p21 protein stability and activity by suppressing ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation
Abstract
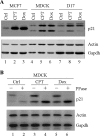
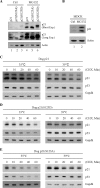
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(Waf1/Cip1) is a major regulator of the cell cycle and plays an important role in many cellular processes, including differentiation, stress response, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. We previously cloned the gene encoding dog p21 and found that unlike its human ortholog, dog p21 is expressed as two isoforms, one high molecular mass band of 23 kDa and one low molecular mass band of 19 kDa. In the current study, we found that the high molecular mass band is phosphorylated, whereas the low molecular mass band is hypophosphorylated. Moreover, by generating multiple mutants of dog p21, we found that serine 123 and proline 124, which form a consensus site for proline-directed phosphorylation, are required for expression of the high molecular mass p21 isoform through phosphorylation at serine 123. Most importantly, we showed that serine 123 phosphorylation inhibits ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation of p21 protein and subsequently, prolongs p21 protein half-life and enhances the ability of p21 to suppress cell proliferation. Taken together, these data reveal that serine 123 phosphorylation modulates p21 protein stability and activity by suppressing ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PPM1D regulates p21 expression via dephoshporylation at serine 123.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(4):641-7. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.994922. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25590690 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-response transition from cell cycle arrest to apoptosis with selective degradation of Mdm2 and p21WAF1/CIP1 in response to the novel anticancer agent, aminoflavone (NSC 686,288).Oncogene. 2007 Jul 19;26(33):4806-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210283. Epub 2007 Feb 12. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17297446
-
S100A11 is involved in the regulation of the stability of cell cycle regulator p21(CIP1/WAF1) in human keratinocyte HaCaT cells.FEBS J. 2013 Aug;280(16):3840-53. doi: 10.1111/febs.12378. Epub 2013 Jun 27. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23745637
-
Ubiquitin-independent degradation of cell-cycle inhibitors by the REGgamma proteasome.Mol Cell. 2007 Jun 22;26(6):843-52. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.05.022. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17588519 Free PMC article.
-
The intricacies of p21 phosphorylation: protein/protein interactions, subcellular localization and stability.Cell Cycle. 2006 Jun;5(12):1313-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.12.2863. Epub 2006 Jun 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16775416 Review.
Cited by
-
CDKN1A/p21 in Breast Cancer: Part of the Problem, or Part of the Solution?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 14;24(24):17488. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417488. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PPM1D regulates p21 expression via dephoshporylation at serine 123.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(4):641-7. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.994922. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25590690 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics of Long-Lived Mammals.Proteomics. 2020 Mar;20(5-6):e1800416. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201800416. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31737995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DAPL1 prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the retinal pigment epithelium and experimental proliferative vitreoretinopathy.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Feb 25;14(2):158. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05693-4. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36841807 Free PMC article.
-
Rbm24, an RNA-binding protein and a target of p53, regulates p21 expression via mRNA stability.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 7;289(6):3164-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.524413. Epub 2013 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24356969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherr C. J., Roberts J. M. (1999) CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1 phase progression. Genes Dev. 13, 1501–1512 - PubMed
-
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. (1993) WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 75, 817–825 - PubMed
-
- el-Deiry W. S., Harper J. W., O'Connor P. M., Velculescu V. E., Canman C. E., Jackman J., Pietenpol J. A., Burrell M., Hill D. E., Wang Y. (1994) WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 54, 1169–1174 - PubMed
-
- Erhardt J. A., Pittman R. N. (1998) Ectopic p21WAF1 expression induces differentiation-specific cell cycle changes in PC12 cells characteristic of nerve growth factor treatment. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 23517–23523 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

