Top-down attention switches coupling between low-level and high-level areas of human visual cortex
- PMID: 22908274
- PMCID: PMC3437858
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1202095109
Top-down attention switches coupling between low-level and high-level areas of human visual cortex
Abstract
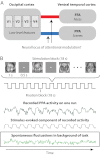
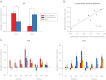
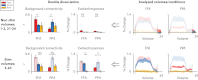
Top-down attention is an essential cognitive ability, allowing our finite brains to process complex natural environments by prioritizing information relevant to our goals. Previous evidence suggests that top-down attention operates by modulating stimulus-evoked neural activity within visual areas specialized for processing goal-relevant information. We show that top-down attention also has a separate influence on the background coupling between visual areas: adopting different attentional goals resulted in specific patterns of noise correlations in the visual system, whereby intrinsic activity in the same set of low-level areas was shared with only those high-level areas relevant to the current goal. These changes occurred independently of evoked activity, persisted without visual stimulation, and predicted behavioral success in deploying attention better than the modulation of evoked activity. This attentional switching of background connectivity suggests that attention may help synchronize different levels of the visual processing hierarchy, forming state-dependent functional pathways in human visual cortex to prioritize goal-relevant information.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mishkin M, Ungerleider LG, Macko KA. Object vision and spatial vision: Two cortical pathways. Trends Neurosci. 1983;6:414–417.
-
- Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1:1–47. - PubMed
-
- Chabris CF, Simons DJ. The Invisible Gorilla: And Other Ways Our Intuitions Deceive Us. New York: Crown Archetype; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

