Targeting and transport: how microtubules control focal adhesion dynamics
- PMID: 22908306
- PMCID: PMC3514042
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201206050
Targeting and transport: how microtubules control focal adhesion dynamics
Abstract
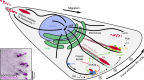
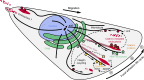
Directional cell migration requires force generation that relies on the coordinated remodeling of interactions with the extracellular matrix (ECM), which is mediated by integrin-based focal adhesions (FAs). Normal FA turnover requires dynamic microtubules, and three members of the diverse group of microtubule plus-end-tracking proteins are principally involved in mediating microtubule interactions with FAs. Microtubules also alter the assembly state of FAs by modulating Rho GTPase signaling, and recent evidence suggests that microtubule-mediated clathrin-dependent and -independent endocytosis regulates FA dynamics. In addition, FA-associated microtubules may provide a polarized microtubule track for localized secretion of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs). Thus, different aspects of the molecular mechanisms by which microtubules control FA turnover in migrating cells are beginning to emerge.
Figures
References
-
- Akhmanova A., Hoogenraad C.C., Drabek K., Stepanova T., Dortland B., Verkerk T., Vermeulen W., Burgering B.M., De Zeeuw C.I., Grosveld F., Galjart N. 2001. Clasps are CLIP-115 and -170 associating proteins involved in the regional regulation of microtubule dynamics in motile fibroblasts. Cell. 104:923–935 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00288-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Applewhite D.A., Grode K.D., Keller D., Zadeh A.D., Slep K.C., Rogers S.L. 2010. The spectraplakin Short stop is an actin-microtubule cross-linker that contributes to organization of the microtubule network. Mol. Biol. Cell. 21:1714–1724 (published erratum appears in Mol. Biol. Cell 2010. 21:2097) 10.1091/mbc.E10-01-0011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

