Hierarchical assembly of the eggshell and permeability barrier in C. elegans
- PMID: 22908315
- PMCID: PMC3514041
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201206008
Hierarchical assembly of the eggshell and permeability barrier in C. elegans
Abstract
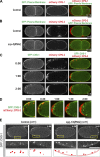
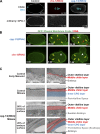
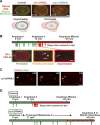
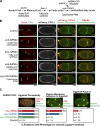
In metazoans, fertilization triggers the assembly of an extracellular coat that constitutes the interface between the embryo and its environment. In nematodes, this coat is the eggshell, which provides mechanical rigidity, prevents polyspermy, and is impermeable to small molecules. Using immunoelectron microscopy, we found that the Caenorhabditis elegans eggshell was composed of an outer vitelline layer, a middle chitin layer, and an inner layer containing chondroitin proteoglycans. The switch between the chitin and proteoglycan layers was achieved by internalization of chitin synthase coincident with exocytosis of proteoglycan-containing cortical granules. Inner layer assembly did not make the zygote impermeable as previously proposed. Instead, correlative light and electron microscopy demonstrated that the permeability barrier was a distinct envelope that formed in a separate step that required fatty acid synthesis, the sugar-modifying enzyme PERM-1, and the acyl chain transfer enzyme DGTR-1. These findings delineate the hierarchy of eggshell assembly and define key molecular mechanisms at each step.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CBD-1 organizes two independent complexes required for eggshell vitelline layer formation and egg activation in C. elegans.Dev Biol. 2018 Oct 15;442(2):288-300. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 30120927 Free PMC article.
-
Eggshell chitin and chitin-interacting proteins prevent polyspermy in C. elegans.Curr Biol. 2010 Nov 9;20(21):1932-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.09.059. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Curr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20971008
-
The eggshell in the C. elegans oocyte-to-embryo transition.Genesis. 2012 Apr;50(4):333-49. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20823. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Genesis. 2012. PMID: 22083685 Review.
-
The C. elegans eggshell.WormBook. 2018 Aug 2;2018:1-36. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.179.1. WormBook. 2018. PMID: 26715360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of the seipin gene perturbs eggshell formation in Caenorhabditiselegans.Development. 2020 Oct 16;147(20):dev192997. doi: 10.1242/dev.192997. Development. 2020. PMID: 32820022 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acid derived signaling in reproduction and development: insights from Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster.Mol Reprod Dev. 2013 Apr;80(4):244-59. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22167. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Mol Reprod Dev. 2013. PMID: 23440886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans Patched domain protein PTR-4 is required for proper organization of the precuticular apical extracellular matrix.Genetics. 2021 Nov 5;219(3):iyab132. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab132. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 34740248 Free PMC article.
-
A sperm-oocyte protein partnership required for egg activation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Development. 2025 Jun 15;152(12):dev204674. doi: 10.1242/dev.204674. Epub 2025 Jun 25. Development. 2025. PMID: 40446215 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term ex ovo culture of Caenorhabditis elegans embryos.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 27:2025.06.26.661779. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.26.661779. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40666948 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The invertebrate Caenorhabditis elegans biosynthesizes ascorbate.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Mar 1;569:32-44. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25668719 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

