IL-1R-MyD88 signaling in keratinocyte transformation and carcinogenesis
- PMID: 22908325
- PMCID: PMC3428947
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20101355
IL-1R-MyD88 signaling in keratinocyte transformation and carcinogenesis
Abstract
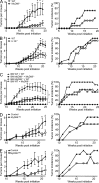
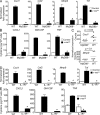
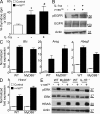
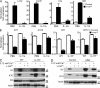
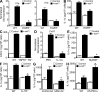
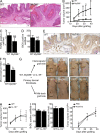
Constitutively active RAS plays a central role in the development of human cancer and is sufficient to induce tumors in two-stage skin carcinogenesis. RAS-mediated tumor formation is commonly associated with up-regulation of cytokines and chemokines that mediate an inflammatory response considered relevant to oncogenesis. In this study, we report that mice lacking IL-1R or MyD88 are less sensitive to topical skin carcinogenesis than their respective wild-type (WT) controls. MyD88(-/-) or IL-1R(-/-) keratinocytes expressing oncogenic RAS are hyperproliferative and fail to up-regulate proinflammatory genes or down-regulate differentiation markers characteristic of RAS-expressing WT keratinocytes. Although RAS-expressing MyD88(-/-) keratinocytes form only a few small tumors in orthotopic grafts, IL-1R-deficient RAS-expressing keratinocytes retain the ability to form tumors in orthotopic grafts. Using both genetic and pharmacological approaches, we find that the differentiation and proinflammatory effects of oncogenic RAS in keratinocytes require the establishment of an autocrine loop through IL-1α, IL-1R, and MyD88 leading to phosphorylation of IκBα and NF-κB activation. Blocking IL-1α-mediated NF-κB activation in RAS-expressing WT keratinocytes reverses the differentiation defect and inhibits proinflammatory gene expression. Collectively, these results demonstrate that MyD88 exerts a cell-intrinsic function in RAS-mediated transformation of keratinocytes.
Figures

Comment in
-
Tumour immunology: Differing roles for MYD88 in carcinogenesis.Nat Rev Immunol. 2012 Oct;12(10):681. doi: 10.1038/nri3304. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22955844 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bar D., Apte R.N., Voronov E., Dinarello C.A., Cohen S. 2004. A continuous delivery system of IL-1 receptor antagonist reduces angiogenesis and inhibits tumor development. FASEB J. 18:161–163 - PubMed
-
- Blumberg H., Dinh H., Trueblood E.S., Pretorius J., Kugler D., Weng N., Kanaly S.T., Towne J.E., Willis C.R., Kuechle M.K., et al. 2007. Opposing activities of two novel members of the IL-1 ligand family regulate skin inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 204:2603–2614 10.1084/jem.20070157 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

