Induction of interleukin-10 is dependent on p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in macrophages infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
- PMID: 22909062
- PMCID: PMC3441385
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-165
Induction of interleukin-10 is dependent on p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in macrophages infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
Abstract
Background: Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) causes reproductive failure and respiratory illness in pigs and usually establishes a persistent infection. Previous studies suggested that interleukin-10 (IL-10) could play a critical role in PRRSV-induced immunosuppression. However, the ability of PRRSV to induce IL-10 in infected cells is controversial. In this study, we further investigated this issue using PRRSV strain CH-1a, which is the first North American genotype strain isolated in China.
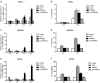
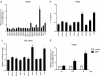
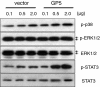
Results: PRRSV strain CH-1a could significantly up-regulate IL-10 production both at mRNA and protein levels in porcine alveolar macrophages (PAMs), bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs), and monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs). However, up-regulation of IL-10 by PRRSV was retarded by specific inhibitors of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) (SB203580) and NF-κB (BAY11-7082). Additionally, p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways but not ERK1/2 MAPK were actually activated in PRRSV-infected BMDMs as demonstrated by western blot analysis, suggesting that p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways are involved in the induction of IL-10 by PRRSV infection. Transfection of PAMs and PAM cell line 3D4/21 (CRL-2843) with viral structural genes showed that glycoprotein5 (GP5) could significantly up-regulate IL-10 production, which was dependent on p38 MAPK and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) activation. We also demonstrated that a full-length glycoprotein was essential for GP5 to induce IL-10 production.
Conclusions: PRRSV strain CH-1a could significantly up-regulate IL-10 production through p38 MAPK activation.
Figures
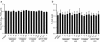
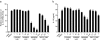
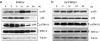

References
-
- Dee SA, Joo HS. Recurrent reproductive failure associated with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome in a swine herd. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 1994;205:1017–1018. - PubMed
-
- Benfield DA, Nelson E, Collins JE, Harris L, Goyal SM, Robison D, Christianson WT, Morrison RB, Gorcyca D, Chladek D. Characterization of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome (SIRS) virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332) Journal of veterinary diagnostic investigation : official publication of the American Association of Veterinary Laboratory Diagnosticians, Inc. 1992;4:127–133. doi: 10.1177/104063879200400202. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Snijder EJ, Meulenberg JJ. The molecular biology of arteriviruses. The Journal of general virology. 1998;79(Pt 5):961–979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

