Placental secretion of interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in preeclampsia: effect of magnesium sulfate
- PMID: 22909148
- PMCID: PMC3438822
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2012.0013
Placental secretion of interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in preeclampsia: effect of magnesium sulfate
Abstract
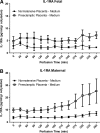
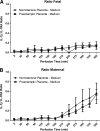
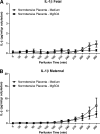
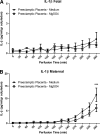
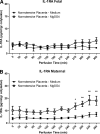
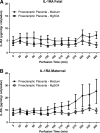
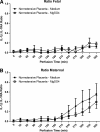
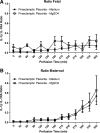
Preeclampsia is a pregnancy-specific disorder characterized by hypertension and systemic endothelial dysfunction. Interleukin (IL)-1β is a possible mediator of maternal endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. Serum IL-1β as well as its natural inhibitor IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) were reported to be increased in women with preeclampsia. In the current study, we addressed the role of the placenta in controlling the circulatory levels of IL-1β and its natural inhibitor IL-1Ra in preeclampsia, and the possible effect of magnesium sulfate (MgSO(4)) on these levels. Using an ex vivo placental perfusion system, placentas from preeclamptic (n = 9) and normotensive (n = 6) pregnancies were perfused in presence or absence of MgSO(4). Perfusate samples were collected from the maternal and the fetal circulations of the perfusion system, and IL-1β and IL-1Ra were examined by enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA). Preeclamptic placentas secreted higher levels of IL-1β (P < 0.001), and a tendentious higher levels of IL-1Ra, mainly into the maternal circulation, as compared with normotensive placentas, although no differences in IL-1β:IL-1Ra ratio were detected. However, there was only tendentious increase in the secretion levels of IL-1β or IL-1Ra into the fetal circulation of preeclamptic placentas, when compared with normotensive placentas. Administration of MgSO(4) to preeclamptic placentas resulted in an attenuation of the increased secretion of IL-1β into the maternal circulation (P < 0.001), and in a tendentious reduction in IL-1Ra. However, IL-1β:IL-1Ra ratio in preeclamptic placentas was not affected by MgSO(4). Interestingly, exposure of normotensive placenta to MgSO(4) resulted only in increased levels of IL-1Ra in the maternal circulation, without affecting IL-1β levels or IL-1β:IL-1Ra ratio. These findings suggest that the placenta may contribute to the elevation in serum IL-1β and IL-1Ra in preeclampsia by increased secretion of these cytokines into the maternal circulation, and that MgSO(4) is able to attenuate this increased secretion of IL-1β, and possibly IL-1Ra, in preeclampsia.
Figures

References
-
- ACOG practice bulletin. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia. Number 33. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;99:159–167. - PubMed
-
- Amash A. Holcberg G. Sheiner E. Huleihel M. Magnesium sulfate normalizes placental interleukin-6 secretion in preeclampsia. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010a;30:683–690. - PubMed
-
- Amash A. Weintraub AY. Sheiner E. Zeadna A. Huleihel M. Holcberg G. Possible therapeutic effect of magnesium sulfate in pre-eclampsia by the down-regulation of placental tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2010b;21:58–64. - PubMed
-
- Benyo DF. Smarason A. Redman CW. Sims C. Conrad KP. Expression of inflammatory cytokines in placentas from women with preeclampsia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:2505–2512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

