The role of glycoprotein H of equine herpesviruses 1 and 4 (EHV-1 and EHV-4) in cellular host range and integrin binding
- PMID: 22909178
- PMCID: PMC3522555
- DOI: 10.1186/1297-9716-43-61
The role of glycoprotein H of equine herpesviruses 1 and 4 (EHV-1 and EHV-4) in cellular host range and integrin binding
Abstract
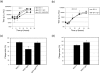
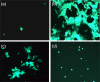
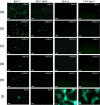
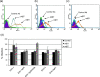
Equine herpesvirus type 1 and 4 (EHV-1 and EHV-4) glycoprotein H (gH) has been hypothesized to play a role in direct fusion of the virus envelope with cellular membranes. To investigate gH's role in infection, an EHV-1 mutant lacking gH was created and the gH genes were exchanged between EHV-1 and EHV-4 to determine if gH affects cellular entry and/or host range. In addition, a serine-aspartic acid-isoleucine (SDI) integrin-binding motif present in EHV-1 gH was mutated as it was presumed important in cell entry mediated by binding to α4β1 or α4β7 integrins. We here document that gH is essential for EHV-1 replication, plays a role in cell-to-cell spread and significantly affects plaque size and growth kinetics. Moreover, we could show that α4β1 and α4β7 integrins are not essential for viral entry of EHV-1 and EHV-4, and that viral entry is not affected in equine cells when the integrins are inaccessible.
Figures


References
-
- King AMQ, Adams MJ, Carstens EB, Lefkowitz EJ. Virus Taxonomy: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. UK: Academic Press, Elsevier; 2012. pp. 114–115.
-
- Telford EA, Watson MS, Perry J, Cullinane AA, Davison AJ. The DNA sequence of equine herpesvirus-4. J Gen Virol. 1998;79:1197–1203. - PubMed
-
- Gryspeerdt AC, Vandekerckhove AP, Garre B, Barbe F, Van de Walle GR, Nauwynck HJ. Differences in replication kinetics and cell tropism between neurovirulent and non-neurovirulent EHV1 strains during the acute phase of infection in horses. Vet Microbiol. 2009;142:242–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

