Genotype-phenotype studies of VCP-associated inclusion body myopathy with Paget disease of bone and/or frontotemporal dementia
- PMID: 22909335
- PMCID: PMC3618576
- DOI: 10.1111/cge.12000
Genotype-phenotype studies of VCP-associated inclusion body myopathy with Paget disease of bone and/or frontotemporal dementia
Abstract
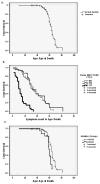
Valosin containing protein (VCP) disease associated with inclusion body myopathy, Paget disease of the bone and frontotemporal dementia is a progressive autosomal dominant disorder caused by mutations in Valosin containing protein gene. To establish genotype-phenotype correlations we analyzed clinical and biochemical markers from a database of 190 members in 27 families harboring 10 missense mutations. Individuals were grouped into three categories: symptomatic, presymptomatic carriers and noncarriers. The symptomatic families were further divided into ten groups based on their VCP mutations. There was marked intra and inter-familial variation; and significant genotype-phenotype correlations were difficult to establish because of small numbers. Nevertheless when comparing the two most common mutations, R155C mutation was found to be more severe, with an earlier onset of myopathy and Paget (p = 0.03). Survival analysis of all subjects revealed an average life span after diagnosis of myopathy and Paget of 18 and 19 years respectively, and after dementia only 6 years. R155C had a reduced survival compared to the R155H mutation (p = 0.03).We identified amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) was diagnosed in 13 individuals (8.9%) and Parkinson's disease in five individuals (3%); however, there was no genotypic correlation. This study represents the largest dataset of patients with VCP disease and expands our understanding of the natural history and provides genotype-phenotype correlations in this unique disease.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Watts GD, Thorne M, Kovach MJ, Pestronk A, Kimonis VE. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in chromosome 9p associated hereditary inclusion body myopathy: exclusion of GNE and three other candidate genes. Neuromuscul Disord. 2003 Sep;13(7–8):559–567. - PubMed
-
- Kovach MJ, Waggoner B, Leal SM, et al. Clinical delineation and localization to chromosome 9p13.3-p12 of a unique dominant disorder in four families: hereditary inclusion body myopathy, Paget disease of bone, and frontotemporal dementia. Molecular genetics and metabolism. 2001 Dec;74(4):458–475. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kimonis V, Donkervoort S, Watts G. GeneTests. University of Washington; Seattle: 2011. Inclusion Body Myopathy Associated with Paget Disease of Bone and/or Frontotemporal Dementia Gene. ( www.genetests.org) [Review] http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20301649.
-
- Nalbandian A, Donkervoort S, Dec E, et al. The multiple faces of valosin-containing protein-associated diseases: inclusion body myopathy with Paget’s disease of bone, frontotemporal dementia, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci. 2011 Nov;45(3):522–531. - PubMed

