Adoptive cell therapy with autologous tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and low-dose Interleukin-2 in metastatic melanoma patients
- PMID: 22909342
- PMCID: PMC3514199
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-169
Adoptive cell therapy with autologous tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and low-dose Interleukin-2 in metastatic melanoma patients
Abstract
Background: Adoptive cell therapy may be based on isolation of tumor-specific T cells, e.g. autologous tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), in vitro activation and expansion and the reinfusion of these cells into patients upon chemotherapy induced lymphodepletion. Together with high-dose interleukin (IL)-2 this treatment has been given to patients with advanced malignant melanoma and impressive response rates but also significant IL-2 associated toxicity have been observed. Here we present data from a feasibility study at a Danish Translational Research Center using TIL adoptive transfer in combination with low-dose subcutaneous IL-2 injections.
Methods: This is a pilot trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00937625) including patients with metastatic melanoma, PS ≤1, age <70, measurable and progressive disease and no involvement of the central nervous system. Six patients were treated with lymphodepleting chemotherapy, TIL infusion, and 14 days of subcutaneous low-dose IL-2 injections, 2 MIU/day.
Results: Low-dose IL-2 considerably decreased the treatment related toxicity with no grade 3-4 IL-2 related adverse events. Objective clinical responses were seen in 2 of 6 treated patients with ongoing complete responses (30+ and 10+ months), 2 patients had stable disease (4 and 5 months) and 2 patients progressed shortly after treatment. Tumor-reactivity of the infused cells and peripheral lymphocytes before and after therapy were analyzed. Absolute number of tumor specific T cells in the infusion product tended to correlate with clinical response and also, an induction of peripheral tumor reactive T cells was observed for 1 patient in complete remission.
Conclusion: Complete and durable responses were induced after treatment with adoptive cell therapy in combination with low-dose IL-2 which significantly decreased toxicity of this therapy.
Figures
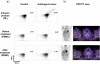
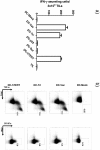
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures. 2010. http://www.cancer.org.
-
- Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC, Akerley W, van den Eertwegh AJ, Lutzky J, Lorigan P, Vaubel JM, Linette GP, Hogg D, Ottensmeier CH, Lebbe C, Peschel C, Quirt I, Clark JI, Wolchok JD, Weber JS, Tian J, Yellin MJ, Nichol GM, Hoos A, Urba WJ. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:711–723. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1003466. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Robert C, Thomas L, Bondarenko I, O'Day S, JW MD, Garbe C, Lebbe C, Baurain JF, Testori A, Grob JJ, Davidson N, Richards J, Maio M, Hauschild A, Miller WH Jr, Gascon P, Lotem M, Harmankaya K, Ibrahim R, Francis S, Chen TT, Humphrey R, Hoos A, Wolchok JD. Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2517–2526. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1104621. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, Hogg D, Lorigan P, Lebbe C, Jouary T, Schadendorf D, Ribas A, O'Day SJ, Sosman JA, Kirkwood JM, Eggermont AM, Dreno B, Nolop K, Li J, Nelson B, Hou J, Lee RJ, Flaherty KT, McArthur GA. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2507–2516. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1103782. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

