Scar/WAVE3 contributes to motility and plasticity of lamellipodial dynamics but not invasion in three dimensions
- PMID: 22909346
- PMCID: PMC3929901
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20112206
Scar/WAVE3 contributes to motility and plasticity of lamellipodial dynamics but not invasion in three dimensions
Abstract
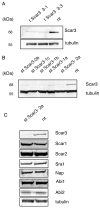
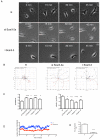
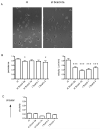
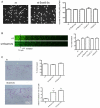
The Scar (suppressor of cAMP receptor)/WAVE [WASP (Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein) verprolin homologous] complex plays a major role in the motility of cells by activating the Arp2/3 complex, which initiates actin branching and drives protrusions. Mammals have three Scar/WAVE isoforms, which show some tissue-specific expression, but their functions have not been differentiated. In the present study we show that depletion of Scar/WAVE3 in the mammalian breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 results in larger and less dynamic lamellipodia. Scar/WAVE3-depleted cells move more slowly but more persistently on a two-dimensional matrix and they typically only show one lamellipod. However, Scar/WAVE3 appears to have no role in driving invasiveness in a three-dimensional Matrigel™ invasion assay or a three-dimensional collagen invasion assay, suggesting that lamellipodial persistence as seen in two-dimensions is not crucial in three-dimensional environments.
Figures
References
-
- Eden S, Rohatgi R, Podtelejnikov AV, Mann M, Kirschner MW. Mechanism of regulation of WAVE1-induced actin nucleation by Rac1 and Nck. Nature. 2002;418:790–793. - PubMed
-
- Machesky LM, Insall RH. Scar1 and the related Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, WASP, regulate the actin cytoskeleton through the Arp2/3 complex. Current biology: CB. 1998;8:1347–1356. - PubMed
-
- Suetsugu S, Miki H, Takenawa T. Identification of two human WAVE/SCAR homologues as general actin regulatory molecules which associate with the Arp2/3 complex. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 1999;260:296–302. - PubMed
-
- Cai X, Xiao T, James SY, Da J, Lin D, Liu Y, Zheng Y, Zou S, Di X, Guo S, et al. Metastatic potential of lung squamous cell carcinoma associated with HSPC300 through its interaction with WAVE2. Lung Cancer. 2009;65:299–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

