A potential role of progestin-induced laminin-5/α6-integrin signaling in the formation of side branches in the mammary gland
- PMID: 22910029
- PMCID: PMC3512027
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2012-1518
A potential role of progestin-induced laminin-5/α6-integrin signaling in the formation of side branches in the mammary gland
Abstract
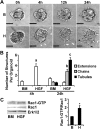
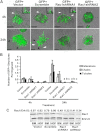
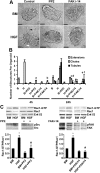
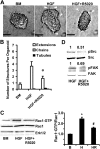
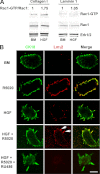
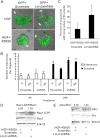
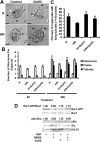
Mammary organoids from adult mice produce tubules, analogous to mammary ducts in vivo, in response to hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) when cultured in collagen gels. The combination of HGF plus progestin (R5020) causes reduced tubule number and length. We hypothesized that the inhibitory effect on tubulogenesis was due to progestin-mediated alteration of HGF/c-Met signaling. Using molecular inhibitors and short hairpin RNA, it was determined that HGF activation of Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate (Rac1) was required for the formation of cytoplasmic extensions, the first step of tubulogenesis, and that Rac1 activity was Src kinase (Src) and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) dependent. The highly novel finding was that R5020 reduced tubulogenesis by up-regulating and increasing extracellular laminin and α6-integrin ligation to reduce activation of the Src, focal adhesion kinase, and Rac1 pathway. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand, another progesterone-induced paracrine factor, did not replicate this effect of R5020. The inhibitory effect of R5020 on tubulogenesis was likely mediated through progesterone receptor (PR) isoform A (PRA), because PRA is the predominant PR isoform expressed in the organoids, and the progestin-induced effect was prevented by the PR antagonist RU486. These results provide a plausible mechanism that explains progestin/PRA-mediated blunting of HGF-induced tubulogenesis in vitro and is proposed to be relevant to progesterone/PRA-induced side-branching in vivo during pregnancy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Progestin-regulated luminal cell and myoepithelial cell-specific responses in mammary organoid culture.Endocrinology. 2008 May;149(5):2098-107. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-1398. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18218689 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct temporal and spatial activities of RU486 on progesterone receptor function in reproductive organs of ovariectomized mice.Endocrinology. 2007 May;148(5):2471-86. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1561. Epub 2007 Feb 15. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17303655
-
Activation of SGK1 by HGF, Rac1 and integrin-mediated cell adhesion in MDCK cells: PI-3K-dependent and -independent pathways.J Cell Sci. 2002 May 1;115(Pt 9):1985-93. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.9.1985. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 11956329
-
HGF induces FAK activation and integrin-mediated adhesion in MTLn3 breast carcinoma cells.Int J Cancer. 1999 Nov 26;83(5):640-9. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19991126)83:5<640::aid-ijc13>3.0.co;2-d. Int J Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10521801
-
Hepatocyte growth factor upregulates alpha2beta1 integrin in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells: implications in tubulogenesis.J Biomed Sci. 2002 May-Jun;9(3):261-72. doi: 10.1007/BF02256073. J Biomed Sci. 2002. PMID: 12065901
Cited by
-
Progesterone stimulates proliferation and promotes cytoplasmic localization of the cell cycle inhibitor p27 in steroid receptor positive breast cancers.Horm Cancer. 2013 Dec;4(6):381-90. doi: 10.1007/s12672-013-0159-5. Epub 2013 Aug 31. Horm Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23996077 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted MicroRNA Profiling Reveals That Exendin-4 Modulates the Expression of Several MicroRNAs to Reduce Steatosis in HepG2 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 18;24(14):11606. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411606. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511368 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal regulation of epithelial organization in a three-dimensional breast tissue culture model.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2014 Jan;20(1):42-51. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2013.0054. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2014. PMID: 23675751 Free PMC article.
-
Role of HGF in epithelial-stromal cell interactions during progression from benign breast disease to ductal carcinoma in situ.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(5):R82. doi: 10.1186/bcr3476. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24025166 Free PMC article.
-
Systems pharmacology of mifepristone (RU486) reveals its 47 hub targets and network: comprehensive analysis and pharmacological focus on FAK-Src-Paxillin complex.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 19;5:7830. doi: 10.1038/srep07830. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25597938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aupperlee MD, Haslam SZ. 2007. Differential hormonal regulation and function of progesterone receptor isoforms in normal adult mouse mammary gland. Endocrinology 148:2290–2300 - PubMed
-
- Lydon JP, DeMayo FJ, Funk CR, Mani SK, Hughes AR, Montgomery CA, Jr, Shyamala G, Conneely OM, O'Malley BW. 1995. Mice lacking progesterone receptor exhibit pleiotropic reproductive abnormalities. Genes Dev 9:2266–2278 - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Valdivia R, Mukherjee A, Ying Y, Li J, Paquet M, DeMayo FJ, Lydon JP. 2009. The RANKL signaling axis is sufficient to elicit ductal side-branching and alveologenesis in the mammary gland of the virgin mouse. Dev Biol 328:127–139 - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Bonizzi G, Seagroves TN, Greten FR, Johnson R, Schmidt EV, Karin M. 2001. IKKalpha provides an essential link between RANK signaling and cyclin D1 expression during mammary gland development. Cell 107:763–775 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

