Phosphatidate phosphatase, a key regulator of lipid homeostasis
- PMID: 22910056
- PMCID: PMC3549317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.08.006
Phosphatidate phosphatase, a key regulator of lipid homeostasis
Abstract
Yeast Pah1p phosphatidate phosphatase (PAP) catalyzes the penultimate step in the synthesis of triacylglycerol. PAP plays a crucial role in lipid homeostasis by controlling the relative proportions of its substrate phosphatidate and its product diacylglycerol. The cellular amounts of these lipid intermediates influence the synthesis of triacylglycerol and the pathways by which membrane phospholipids are synthesized. Physiological functions affected by PAP activity include phospholipid synthesis gene expression, nuclear/endoplasmic reticulum membrane growth, lipid droplet formation, and vacuole homeostasis and fusion. Yeast lacking Pah1p PAP activity are acutely sensitive to fatty acid-induced toxicity and exhibit respiratory deficiency. PAP is distinguished in its cellular location, catalytic mechanism, and physiological functions from Dpp1p and Lpp1p lipid phosphate phosphatases that utilize a variety of substrates that include phosphatidate. Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation is a major mechanism by which Pah1p PAP activity is regulated. Pah1p is phosphorylated by cytosolic-associated Pho85p-Pho80p, Cdc28p-cyclin B, and protein kinase A and is dephosphorylated by the endoplasmic reticulum-associated Nem1p-Spo7p phosphatase. The dephosphorylation of Pah1p stimulates PAP activity and facilitates the association with the membrane/phosphatidate allowing for its reaction and triacylglycerol synthesis. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled Phospholipids and Phospholipid Metabolism.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


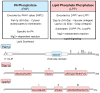
 , approximate positions of the sites (Ser110, Ser114, Ser168, Ser602, Thr723, Ser744, and Ser748) phosphorylated by Pho85p-Pho80p; ★, approximate positions of the sites (Ser602, Thr723, and Ser744) phosphorylated by Cdc28p-cyclin B;
, approximate positions of the sites (Ser110, Ser114, Ser168, Ser602, Thr723, Ser744, and Ser748) phosphorylated by Pho85p-Pho80p; ★, approximate positions of the sites (Ser602, Thr723, and Ser744) phosphorylated by Cdc28p-cyclin B;
 , approximate positions of the sites (Ser10, Ser677, Ser773, Ser774, and Ser788) phosphorylated by protein kinase A. The diagrams of each protein are not drawn to scale.
, approximate positions of the sites (Ser10, Ser677, Ser773, Ser774, and Ser788) phosphorylated by protein kinase A. The diagrams of each protein are not drawn to scale.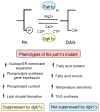
References
-
- Smith SW, Weiss SB, Kennedy EP. The enzymatic dephosphorylation of phosphatidic acids. J Biol Chem. 1957;228:915–922. - PubMed
-
- Brindley DN. Intracellular translocation of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase and its possible role in the control of glycerolipid synthesis. Prog Lipid Res. 1984;23:115–133. - PubMed
-
- Nanjundan M, Possmayer F. Pulmonary phosphatidic acid phosphatase and lipid phosphate phosphohydrolase. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;284:L1–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

