The chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy outcome measures standardization study: from consensus to the first validity and reliability findings
- PMID: 22910842
- PMCID: PMC3551481
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mds329
The chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy outcome measures standardization study: from consensus to the first validity and reliability findings
Abstract
Background: Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a debilitating and dose-limiting complication of cancer treatment. Thus far, the impact of CIPN has not been studied in a systematic clinimetric manner. The objective of the study was to select outcome measures for CIPN evaluation and to establish their validity and reproducibility in a cross-sectional multicenter study.
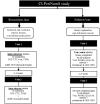
Patients and methods: After literature review and a consensus meeting among experts, face/content validity were obtained for the following selected scales: the National Cancer Institute-Common Toxicity Criteria (NCI-CTC), the Total Neuropathy Score clinical version (TNSc), the modified Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment (INCAT) group sensory sumscore (mISS), the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) QLQ-C30, and CIPN20 quality-of-life measures. A total of 281 patients with stable CIPN were examined. Validity (correlation) and reliability studies were carried out.
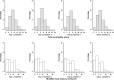
Results: Good inter-/intra-observer scores were obtained for the TNSc, mISS, and NCI-CTC sensory/motor subscales. Test-retest values were also good for the EORTC QLQ-C30 and CIPN20. Acceptable validity scores were obtained through the correlation among the measures.
Conclusion: Good validity and reliability scores were demonstrated for the set of selected impairment and quality-of-life outcome measures in CIPN. Future studies are planned to investigate the responsiveness aspects of these measures.
Figures


References
-
- Cavaletti G, Frigeni B, Lanzani F, et al. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity assessment: a critical revision of the currently available tools. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:479–494. - PubMed
-
- Markman M. Chemotherapy-associated neurotoxicity: an important side effect-impacting on quality, rather than quantity, of life. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1996;122:511–512. - PubMed
-
- Wenzel L, Vergote I, Cella D. Quality of life in patients receiving treatment for gynecologic malignancies: special considerations for patient care. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2003;83(Suppl 1):211–229. - PubMed
-
- Streiner DL, Norman GR. Health Measurement Scales. A Practical Guide to their Development and Use. New York: Oxford University Press; 1998.
-
- Liang MH. Evaluating measurement responsiveness. J Rheumatol. 1995;22:1191–1192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

