The requirement of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 in regulation of hypoxia-inducing factor-1α mRNA stability
- PMID: 22910906
- PMCID: PMC3464542
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.365882
The requirement of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 in regulation of hypoxia-inducing factor-1α mRNA stability
Abstract
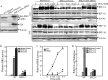
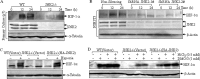
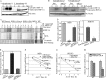
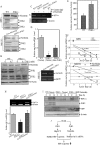
The mRNA of hif-1α is considered as being constitutively and ubiquitously expressed, regardless of the level of oxygen tension. However many recent reports have showed that hif-1α mRNA could be regulated by natural antisense transcripts, potential microRNAs, and low O(2). In this study, it was found that a deficiency of JNK2 expression reduced HIF-1α protein induction in response to nickel treatment resulting from the impaired expression of hif-1α mRNA. Both the promoter luciferase assay and mRNA degradation assay clearly showed that depletion of JNK2 affected stability of hif-1α mRNA, rather than regulated its transcription. In addition, nucleolin, a classic histone chaperone, was demonstrated to physically bind to hif-1α mRNA and maintain its stability. Further investigation indicated that JNK2 regulated nucleolin expression and might in turn stabilize hif-1α mRNA. Collectively, we provided one more piece of evidence for the oncogenic role of JNK2 and nucleolin in regulating the cancer microenvironments by controlling HIF-1α expression.
Figures

References
-
- Grandjean P. (1984) Human exposure to nickel. IARC. Sci. Publ. 53, 469–485 - PubMed
-
- Furst A. (1984) Mechanism of action of nickel as a carcinogen: needed information. IARC. Sci. Publ. 53, 245–252 - PubMed
-
- Lu H., Shi X., Costa M., Huang C. (2005) Carcinogenic effect of nickel compounds. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 279, 45–67 - PubMed
-
- Ke Q., Costa M. (2006) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol. Pharmacol. 70, 1469–1480 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

