Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) breast cancer susceptibility loci in Arabs: susceptibility and prognostic implications in Tunisians
- PMID: 22910930
- PMCID: PMC3439608
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-012-2202-6
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) breast cancer susceptibility loci in Arabs: susceptibility and prognostic implications in Tunisians
Abstract
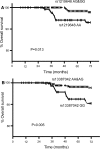
Genome-wide Association Studies (GWAS) revealed novel genetic markers for breast cancer susceptibility. But little is known about the risk factors and molecular events associated with breast cancer in Arab Population. Therefore, we designed a broad study to investigate the susceptibility and prognostic implications of the GWAS breast cancer loci in the Tunisian population. In a cohort of 640 unrelated patients with breast cancer and 371 healthy control subjects, we characterized the variation of 9 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), namely rs1219648, rs2981582; rs8051542, rs12443621, and rs3803662; rs889312; rs3817198; rs13387042 and rs13281615. Only 5 out of 9 GWAS breast cancer loci were found to be significantly associated with breast cancer in Tunisians: The rs1219648 (G vs. A allele: OR = 1.36, P = 1 × 10(-3)) and rs2981582 (A vs. G allele: OR = 1.55, P = 3 × 10(-6)) of FGFR2 gene; the rs8051542 of the TNRC9 gene (T vs. C allele: OR = 1.40, P = 4 × 10(-4)); the rs889312 of the MAP3K1 gene (C vs. A allele: OR = 1.33, P = 3 × 10(-3)) and the rs13281615 located on 8q24 (G vs. A allele: OR = 1.21, P = 0.03). Homozygous variant genotypes of rs2981582 were strongly related to lymph node negative breast cancer (OR = 3.33, P = 6 × 10(-7)) and the minor allele of rs2981582 was associated with increased risk of ER+ tumors (OR = 1.57, P = 0.02; OR = 2.15, P = 0.001, for heterozygous and homozygous variant genotypes, respectively) and increased risk of distant metastasis development (OR = 2.30, P = 4 × 10(-3); OR = 3.57, P = 6 × 10(-5), for heterozygous and homozygous variant genotypes, respectively) in a dose dependent manner. The association for rs8051542 was stronger for high-grade SBR tumors (OR = 2.54, P = 2 × 10(-4)). GG genotype of rs13387042 on 2q35 showed a significant association with the risk of developing distant metastasis (OR = 1.94, P = 0.02). The G allele of rs1219648 in FGFR2 and the A allele of rs13387042 on 2q35 indicated a better prognosis by showing a significantly higher overall survival rates (P = 0.013 and P = 0.005, respectively). In conclusion, GWAS breast cancer FGFR2, TNRC9, MAP3K1, and 8q24 loci are associated with an increased risk of breast cancer and genetic variation in FGFR2 gene may predict the aggressiveness of breast cancer in Tunisians.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Replication of five GWAS-identified loci and breast cancer risk among Hispanic and non-Hispanic white women living in the Southwestern United States.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Sep;129(2):531-9. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1498-y. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21475998 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of breast cancer associations with five susceptibility loci by clinical and pathological characteristics.PLoS Genet. 2008 Apr 25;4(4):e1000054. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000054. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18437204 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical correlates of low-risk variants in FGFR2, TNRC9, MAP3K1, LSP1 and 8q24 in a Dutch cohort of incident breast cancer cases.Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9(6):R78. doi: 10.1186/bcr1793. Breast Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17997823 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer genome-wide association studies: there is strength in numbers.Oncogene. 2012 Apr 26;31(17):2121-8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.408. Epub 2011 Sep 26. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 21996731 Review.
-
Genetic susceptibility loci for breast cancer by estrogen receptor status.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Dec 15;14(24):8000-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0975. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19088016 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding genetic variations associated with familial breast cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Oct 10;22(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03553-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39390525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of three SNPs in TOX3 and breast cancer risk: Evidence from 97275 cases and 128686 controls.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 4;5:12773. doi: 10.1038/srep12773. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26239137 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative assessment of 2q35-rs13387042 polymorphism and hormone receptor status with breast cancer risk.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 22;8(7):e66979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066979. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23894282 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of Breast Cancer Associations with Common Genetic Variants in FGFR2 according to the Intrinsic Subtypes in Southern Han Chinese Women.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:626948. doi: 10.1155/2015/626948. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26421298 Free PMC article.
-
TNRC9 rs12443621 and FGFR2 rs2981582 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Feb 24;14(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0795-7. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26911390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Curado MP, Edwards B, Shin HR. Cancer incidence in five continents. Lyon: IARC Scientific Publications; 2007.
-
- Ferlay J, Parkin DM, Steliarova-Foucher E (2010) GLOBOCAN 2008. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide IARC Cancer Base No. 10. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon. http://globocan.iarc.fr
-
- Missaoui N, Jaidene L, Abdelkrim SB, Abdelkader AB, Beizig N, Yaacoub LB, Yaacoubi MT, Hmissa S. Breast cancer in Tunisia: clinical and pathological findings. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12:169–172. - PubMed
-
- Antoniou A, Pharoah PD, Narod S, Risch HA, Eyfjord JE, Hopper JL, Loman N, Olsson H, Johannsson O, Borg A, et al. Average risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations detected in case Series unselected for family history: a combined analysis of 22 studies. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;72:1117–1130. doi: 10.1086/375033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous