The dynamics, causes and possible prevention of Hepatitis E outbreaks
- PMID: 22911752
- PMCID: PMC3404073
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041135
The dynamics, causes and possible prevention of Hepatitis E outbreaks
Abstract
Rapidly spreading infectious diseases are a serious risk to public health. The dynamics and the factors causing outbreaks of these diseases can be better understood using mathematical models, which are fit to data. Here we investigate the dynamics of a Hepatitis E outbreak in the Kitgum region of northern Uganda during 2007 to 2009. First, we use the data to determine that R0 is approximately 2.25 for the outbreak. Secondly, we use a model to estimate that the critical level of latrine and bore hole coverages needed to eradicate the epidemic is at least 16% and 17% respectively. Lastly, we further investigate the relationship between the co-infection factor for malaria and Hepatitis E on the value of R0 for Hepatitis E. Taken together, these results provide us with a better understanding of the dynamics and possible causes of Hepatitis E outbreaks.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

 .
.
 is 2,
is 2,  , and
, and  . Other parameter values are given in Table 2.
. Other parameter values are given in Table 2.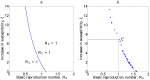
 against increase in susceptibility to Hepatitis E of malaria infected individuals is shown in (b),
against increase in susceptibility to Hepatitis E of malaria infected individuals is shown in (b),  , using parameters estimated from fitting tool.
, using parameters estimated from fitting tool.References
-
- Cyranoski D. Outbreak of chicken flu rattles Hong Kong. Nature. 2004;412:261. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald G. The Epidemiology and Control of Malaria. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 1957.
-
- Kermack WO, McKendrick AG. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc R Soc London. 1927;115:700–721.
-
- King AA, Ionides EL, Pascual M, Bouma MJ. Inapparent infections and cholera dynamics. Nature. 2008;454(7206):877–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

