Aldolase B knockdown prevents high glucose-induced methylglyoxal overproduction and cellular dysfunction in endothelial cells
- PMID: 22911800
- PMCID: PMC3404030
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041495
Aldolase B knockdown prevents high glucose-induced methylglyoxal overproduction and cellular dysfunction in endothelial cells
Abstract
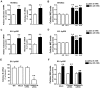
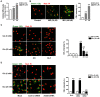
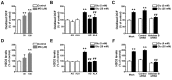
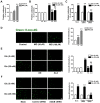
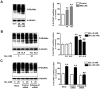
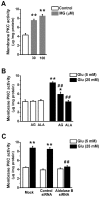
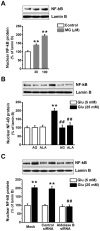
We used cultured endothelial cells as a model to examine whether up-regulation of aldolase B and enhanced methylglyoxal (MG) formation play an important role in high glucose-induced overproduction of advanced glycosylation endproducts (AGEs), oxidative stress and cellular dysfunction. High glucose (25 mM) incubation up-regulated mRNA levels of aldose reductase (an enzyme converting glucose to fructose) and aldolase B (a key enzyme that catalyzes MG formation from fructose) and enhanced MG formation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and HUVEC-derived EA. hy926 cells. High glucose-increased MG production in EA. hy926 cells was completely prevented by siRNA knockdown of aldolase B, but unaffected by siRNA knockdown of aldolase A, an enzyme responsible for MG formation during glycolysis. In addition, inhibition of cytochrome P450 2E1 or semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase which produces MG during the metabolism of lipid and proteins, respectively, did not alter MG production. Both high glucose (25 mM) and MG (30, 100 µM) increased the formation of N(ε)-carboxyethyl-lysine (CEL, a MG-induced AGE), oxidative stress (determined by the generation of oxidized DCF, H(2)O(2), protein carbonyls and 8-oxo-dG), O-GlcNAc modification (product of the hexosamine pathway), membrane protein kinase C activity and nuclear translocation of NF-κB in EA. hy926 cells. However, the above metabolic and signaling alterations induced by high glucose were completely prevented by knockdown of aldolase B and partially by application of aminoguanidine (a MG scavenger) or alagebrium (an AGEs breaker). In conclusion, efficient inhibition of aldolase B can prevent high glucose-induced overproduction of MG and related cellular dysfunction in endothelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Brownlee M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 2001;414:813–820. - PubMed
-
- Hanssen KF. Blood glucose control and microvascular and macrovascular complications in diabetes. Diabetes. 1997;46:S101–103. - PubMed
-
- Scalia R, Gong Y, Berzins B, Zhao LJ, Sharma K. Hyperglycemia is a major determinant of albumin permeability in diabetic microcirculation: the role of mu-calpain. Diabetes. 2007;56:1842–1849. - PubMed
-
- Schalkwijk CG, Stehouwer CD. Vascular complications in diabetes mellitus: the role of endothelial dysfunction. Clin Sci (Lond) 2005;109:143–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

