Cross-talk between the fat body and brain regulates insect developmental arrest
- PMID: 22912402
- PMCID: PMC3437847
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1212879109
Cross-talk between the fat body and brain regulates insect developmental arrest
Abstract
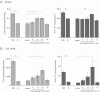
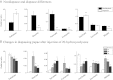
Developmental arrest, a critical component of the life cycle in animals as diverse as nematodes (dauer state), insects (diapause), and vertebrates (hibernation), results in dramatic depression of the metabolic rate and a profound extension in longevity. Although many details of the hormonal systems controlling developmental arrest are well-known, we know little about the interactions between metabolic events and the hormones controlling the arrested state. Here, we show that diapause is regulated by an interplay between blood-borne metabolites and regulatory centers within the brain. Gene expression in the fat body, the insect equivalent of the liver, is strongly suppressed during diapause, resulting in low levels of tricarboxylic acid (TCA) intermediates circulating within the blood, and at diapause termination, the fat body becomes activated, releasing an abundance of TCA intermediates that act on the brain to stimulate synthesis of regulatory peptides that prompt production of the insect growth hormone ecdysone. This model is supported by our success in breaking diapause by injecting a mixture of TCA intermediates and upstream metabolites. The results underscore the importance of cross-talk between the brain and fat body as a regulator of diapause and suggest that the TCA cycle may be a checkpoint for regulating different forms of animal dormancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang Q, Denlinger DL. Dynamics of diapause hormone and prothoracicotropic hormone transcript expression at diapause termination in pupae of the corn earworm, Helicoverpa zea. Peptides. 2012;34:120–126. - PubMed
-
- Denlinger DL, Yocum GD, Rinehart JP. In: Comprehensive Insect Molecular Science. Gilbert LI, Iatrou K, Gill SS, editors. Vol 3. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2005. pp. 615–650.
-
- Kostál V. Eco-physiological phases of insect diapause. J Insect Physiol. 2006;52:113–127. - PubMed
-
- Hu PJ. 2007. The C. elegans Research Community, WormBook. Available at http://www.wormbook.org. Accessed August 8, 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

