Diabetogenic T-cell clones recognize an altered peptide of chromogranin A
- PMID: 22912420
- PMCID: PMC3501882
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-0112
Diabetogenic T-cell clones recognize an altered peptide of chromogranin A
Abstract
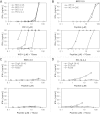
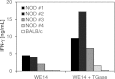
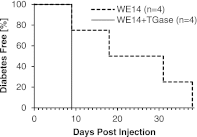
Chromogranin A (ChgA) has been identified as the antigen target for three NOD-derived, diabetogenic CD4 T-cell clones, including the well-known BDC-2.5. These T-cell clones respond weakly to the peptide WE14, a naturally occurring proteolytic cleavage product from ChgA. We show here that WE14 can be converted into a highly antigenic T-cell epitope through treatment with the enzyme transglutaminase (TGase). The WE14 responses of three NOD-derived CD4 T-cell clones, each with different T-cell receptors (TCRs), and of T cells from BDC-2.5 TCR transgenic mice are increased after TGase conversion of the peptide. Primary CD4 T cells isolated from NOD mice also respond to high concentrations of WE14 and significantly lower concentrations of TGase-treated WE14. We hypothesize that posttranslational modification plays a critical role in the generation of T-cell epitopes in type 1 diabetes.
Figures



References
-
- Haskins K. Pathogenic T-cell clones in autoimmune diabetes: more lessons from the NOD mouse. Adv Immunol 2005;87:123–162 - PubMed
-
- Curry WJ, Barkatullah SC, Johansson AN, et al. WE-14, a chromogranin a-derived neuropeptide. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2002;971:311–316 - PubMed
-
- Lorand L, Graham RM. Transglutaminases: crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003;4:140–156 - PubMed
-
- Nikoopour E, Sandrock C, Huszarik K, et al. Cutting edge: vasostatin-1-derived peptide ChgA29-42 is an antigenic epitope of diabetogenic BDC2.5 T cells in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol 2011;186:3831–3835 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

