Drosophila Hox and sex-determination genes control segment elimination through EGFR and extramacrochetae activity
- PMID: 22912593
- PMCID: PMC3415437
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002874
Drosophila Hox and sex-determination genes control segment elimination through EGFR and extramacrochetae activity
Abstract
The formation or suppression of particular structures is a major change occurring in development and evolution. One example of such change is the absence of the seventh abdominal segment (A7) in Drosophila males. We show here that there is a down-regulation of EGFR activity and fewer histoblasts in the male A7 in early pupae. If this activity is elevated, cell number increases and a small segment develops in the adult. At later pupal stages, the remaining precursors of the A7 are extruded under the epithelium. This extrusion requires the up-regulation of the HLH protein Extramacrochetae and correlates with high levels of spaghetti-squash, the gene encoding the regulatory light chain of the non-muscle myosin II. The Hox gene Abdominal-B controls both the down-regulation of spitz, a ligand of the EGFR pathway, and the up-regulation of extramacrochetae, and also regulates the transcription of the sex-determining gene doublesex. The male Doublesex protein, in turn, controls extramacrochetae and spaghetti-squash expression. In females, the EGFR pathway is also down-regulated in the A7 but extramacrochetae and spaghetti-squash are not up-regulated and extrusion of precursor cells is almost absent. Our results show the complex orchestration of cellular and genetic events that lead to this important sexually dimorphic character change.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
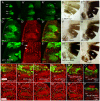

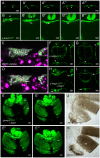
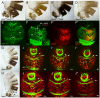
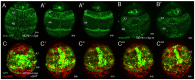

References
-
- Williams TM, Carroll SB (2009) Genetic and molecular insights into the development and evolution of sexual dimorphism. Nat Rev Genet 10: 797–804. - PubMed
-
- Pearson JC, Lemons D, McGinnis W (2005) Modulating Hox gene functions during animal body patterning. Nat Rev Genet 6: 893–904. - PubMed
-
- Sánchez-Herrero E, Vernós I, Marco R, Morata G (1985) Genetic organization of Drosophila bithorax complex. Nature 313: 108–113. - PubMed
-
- Tiong S, Bone LM, Whittle RS (1985) Recessive lethal mutations within the bithorax-complex in Drosophila . Mol Gen Genet 200: 335–342. - PubMed
-
- Casanova J, Sánchez-Herrero E, Morata G (1985) Identification and characterization of a parasegment specific regulatory element of the Abdominal-B gene of Drosophila. Cell 47: 627–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

