Overexpression of guanylate cyclase activating protein 2 in rod photoreceptors in vivo leads to morphological changes at the synaptic ribbon
- PMID: 22912773
- PMCID: PMC3418235
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042994
Overexpression of guanylate cyclase activating protein 2 in rod photoreceptors in vivo leads to morphological changes at the synaptic ribbon
Abstract
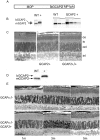
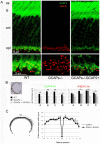
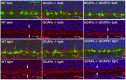
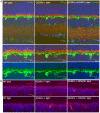
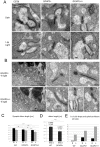
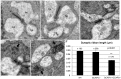
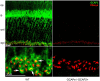
Guanylate cyclase activating proteins are EF-hand containing proteins that confer calcium sensitivity to retinal guanylate cyclase at the outer segment discs of photoreceptor cells. By making the rate of cGMP synthesis dependent on the free intracellular calcium levels set by illumination, GCAPs play a fundamental role in the recovery of the light response and light adaptation. The main isoforms GCAP1 and GCAP2 also localize to the synaptic terminal, where their function is not known. Based on the reported interaction of GCAP2 with Ribeye, the major component of synaptic ribbons, it was proposed that GCAP2 could mediate the synaptic ribbon dynamic changes that happen in response to light. We here present a thorough ultrastructural analysis of rod synaptic terminals in loss-of-function (GCAP1/GCAP2 double knockout) and gain-of-function (transgenic overexpression) mouse models of GCAP2. Rod synaptic ribbons in GCAPs-/- mice did not differ from wildtype ribbons when mice were raised in constant darkness, indicating that GCAPs are not required for ribbon early assembly or maturation. Transgenic overexpression of GCAP2 in rods led to a shortening of synaptic ribbons, and to a higher than normal percentage of club-shaped and spherical ribbon morphologies. Restoration of GCAP2 expression in the GCAPs-/- background (GCAP2 expression in the absence of endogenous GCAP1) had the striking result of shortening ribbon length to a much higher degree than overexpression of GCAP2 in the wildtype background, as well as reducing the thickness of the outer plexiform layer without affecting the number of rod photoreceptor cells. These results indicate that preservation of the GCAP1 to GCAP2 relative levels is relevant for maintaining the integrity of the synaptic terminal. Our demonstration of GCAP2 immunolocalization at synaptic ribbons at the ultrastructural level would support a role of GCAPs at mediating the effect of light on morphological remodeling changes of synaptic ribbons.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Presynaptic [Ca(2+)] and GCAPs: aspects on the structure and function of photoreceptor ribbon synapses.Front Mol Neurosci. 2014 Feb 6;7:3. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00003. eCollection 2014. Front Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24567702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guanylate cyclase-activating protein 2 contributes to phototransduction and light adaptation in mouse cone photoreceptors.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 11;293(19):7457-7465. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001574. Epub 2018 Mar 16. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29549122 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent binding of the neuronal Ca2+ sensor protein GCAP2 to photoreceptor synaptic ribbons.J Neurosci. 2010 May 12;30(19):6559-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3701-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20463219 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic relay mechanism stimulates cyclic GMP synthesis in rod photoresponse: biochemical and physiological study in guanylyl cyclase activating protein 1 knockout mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047637. Epub 2012 Oct 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23082185 Free PMC article.
-
Mg2+/Ca2+ cation binding cycle of guanylyl cyclase activating proteins (GCAPs): role in regulation of photoreceptor guanylyl cyclase.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Jan;334(1-2):117-24. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0328-6. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19953307 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lateral Inhibition in the Vertebrate Retina: The Case of the Missing Neurotransmitter.PLoS Biol. 2015 Dec 10;13(12):e1002322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002322. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Biol. 2015. PMID: 26656622 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic [Ca(2+)] and GCAPs: aspects on the structure and function of photoreceptor ribbon synapses.Front Mol Neurosci. 2014 Feb 6;7:3. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00003. eCollection 2014. Front Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24567702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional EF-hands in neuronal calcium sensor GCAP2 determine its phosphorylation state and subcellular distribution in vivo, and are essential for photoreceptor cell integrity.PLoS Genet. 2014 Jul 24;10(7):e1004480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004480. eCollection 2014 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25058152 Free PMC article.
-
A calcium-relay mechanism in vertebrate phototransduction.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Jun 19;4(6):909-17. doi: 10.1021/cn400027z. Epub 2013 Mar 21. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23472635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single Ca2+ channels and exocytosis at sensory synapses.J Physiol. 2013 Jul 1;591(13):3167-78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.249482. Epub 2013 Mar 4. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23459757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parsons TD, Sterling P (2003) Synaptic ribbon. Conveyor belt or safety belt? Neuron 37: 379–382. - PubMed
-
- Prescott ED, Zenisek D (2005) Recent progress towards understanding the synaptic ribbon. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15: 431–436. - PubMed
-
- von Gersdorff H (2001) Synaptic ribbons: versatile signal transducers. Neuron 29: 7–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

