Hmgb3 is regulated by microRNA-206 during muscle regeneration
- PMID: 22912879
- PMCID: PMC3422271
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043464
Hmgb3 is regulated by microRNA-206 during muscle regeneration
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been recently involved in most of human diseases as targets for potential strategies to rescue the pathological phenotype. Since the skeletal muscle is a spread-wide highly differentiated and organized tissue, rescue of severely compromised muscle still remains distant from nowadays. For this reason, we aimed to identify a subset of miRNAs major involved in muscle remodelling and regeneration by analysing the miRNA-profile of single fibres isolated from dystrophic muscle, which was here considered as a model of chronic damage.
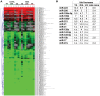
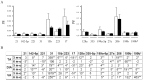
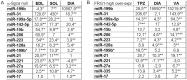
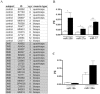
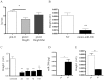
Methodology/principal findings: The miRNA-signature associated to regenerating (newly formed) and remodelling (resting) fibres was investigated in animal models of muscular dystrophies and acute damage, in order to distinguish which miRNAs are primary related to muscle regeneration. In this study we identify fourteen miRNAs associated to dystrophic fibres responsible for muscle regeneration and remodelling, and confirm over-expression of the previously identified regeneration-associated myomiR-206. In particular, a functional binding site for myomiR-206 was identified and validated in the 3'untranslated region (3'UTR) of an X-linked member of a family of sequence independent chromatin-binding proteins (Hmgb3) that is preferentially expressed in hematopoietic stem cells. During regeneration of single muscle fibres, Hmgb3 messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein expression was gradually reduced, concurrent with the up-regulation of miR-206.
Conclusion/significance: Our results elucidate a negative feedback circuit in which myomiR-206 represses Hmgb3 expression to modulate the regeneration of single muscle fibres after acute and chronic muscle damage. These findings suggest that myomiR-206 may be a potential therapeutic target in muscle diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
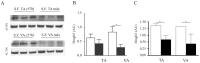

References
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297. - PubMed
-
- Singh SK, Pal Bhadra M, Girschick HJ, Bhadra U (2008) MicroRNAs–micro in size but macro in function. Febs J 275: 4929–4944. - PubMed
-
- Crist CG, Buckingham M (2009) Megarole for microRNA in muscle disease Cell Metab. 12: 425–426. - PubMed
-
- Thum T, Gross C, Fiedler J, Fischer T, Kissler S, et al. (2008) MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts Nature. 456: 980–984. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

