Are Multimorbidities Underestimated in Scoring Systems of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Like in SCORTEN?
- PMID: 22912906
- PMCID: PMC3411276
Are Multimorbidities Underestimated in Scoring Systems of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Like in SCORTEN?
Abstract
Objective: Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome have related high morbidity and mortality. We predict that preexisting multimorbidity is a major prognostic factor of both these diseases.
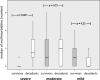
Methods: A retrospective analysis in toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome patients over the past 10 years. Three severity categories (minor, moderate, and severe multimorbidity) were defined according to a point-rating system.
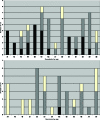
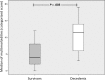
Results: Twenty-seven inpatients, with a median age of 63 years, diagnosed with toxic epidermal necrolysis (n = 13) or Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (n = 14) were assessed in this study. Of these, 14 patients died during the course of the study. Nonsurvivors showed significantly higher multimorbidity (P = .038), with higher scoring on the points system for disease severity (P = .003), than survivors and CART (Classification and Regression Trees) cross-validation (P < .05).
Limitations: Restricted number of patients due to low prevalence rate.
Conclusion: The complexity of associated multimorbidity appears to have a large influence on toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome prognosis, which has not been considered in any of the established scoring systems.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness, safety and tolerability of cyclosporine versus supportive treatment in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A record-based study.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017 May-Jun;83(3):312-316. doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_201_16. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017. PMID: 28366923
-
Evaluation of the patients diagnosed with Stevens Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a single center experience.Turk Pediatri Ars. 2016 Sep 1;51(3):152-158. doi: 10.5152/TurkPediatriArs.2016.3836. eCollection 2016 Sep. Turk Pediatri Ars. 2016. PMID: 27738400 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of reporting of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in association with selective COX-2 inhibitors.Drug Saf. 2005;28(10):917-24. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200528100-00008. Drug Saf. 2005. PMID: 16180941
-
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a review of the literature.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005 Apr;94(4):419-36; quiz 436-8, 456. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61112-X. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15875523 Review.
-
Accuracy of SCORTEN to predict the prognosis of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Sep;34(9):2066-2077. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16137. Epub 2020 Jan 7. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020. PMID: 31912590
Cited by
-
Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Aug;10(2):519-524. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2549. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26622347 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous Drug Reactions in the Elderly.Drugs Aging. 2017 Sep;34(9):655-672. doi: 10.1007/s40266-017-0483-5. Drugs Aging. 2017. PMID: 28801750 Review.
-
Stevens-Johnson syndrome / toxic epidermal necrolysis: an Asia-Pacific perspective.Asia Pac Allergy. 2013 Oct;3(4):215-23. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2013.3.4.215. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Asia Pac Allergy. 2013. PMID: 24260726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intravenous Immunoglobulin Combined With Corticosteroids for the Treatment of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Propensity-Matched Retrospective Study in China.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 18;12:750173. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.750173. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35115922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breiman L, Friedman J, Olshen R, Stone C. Classification and Regression Trees (CART) Pacific Grove, CA: Wadsworth; 1984.
-
- Breiman L, Friedman J, Olshen R, Stone C. CART (Version 4.0) Pacific Grove, CA: Wadsworth; 1997.
-
- Rzany B, Hering O, Mockenhaupt M, et al. Histopathological and epidemiological characteristics of patients with erythema exudativum multiforme major, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:6–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
