Managing gastroesophageal reflux disease in children: The role of endoscopy
- PMID: 22912907
- PMCID: PMC3423514
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i8.339
Managing gastroesophageal reflux disease in children: The role of endoscopy
Abstract
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a growing problem in the pediatric population and recent advances in diagnostics and therapeutics have improved their management, particularly the use of esophago-gastroduodenoscopy (EGD). Most of the current knowledge is derived from studies in adults; however there are distinct features between infant onset and adult onset GERD. Children are not just little adults and attention must be given to the stages of growth and development and how these stages impact the disease management. Although there is a lack of a gold standard test to diagnose GERD in children, EGD with biopsy is essential to assess the type and severity of tissue damage. To date, the role of endoscopy in adults and children has been to assess the extent of esophagitis and detect metaplastic changes complicating GERD; however the current knowledge points another role for the EGD with biopsy that is to rule out other potential causes of esophagitis in patients with GERD symptoms such as eosinophilic esophagitis. This review highlights special considerations about the role of EGD in the management of children with GERD.
Keywords: Children; Endoscopy; Esophagitis; Gastroesophageal reflux; Infants.
Figures
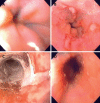
References
-
- Vakil N. Disease definition, clinical manifestations, epidemiology and natural history of GERD. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;24:759–764. - PubMed
-
- Ryan AM, Duong M, Healy L, Ryan SA, Parekh N, Reynolds JV, Power DG. Obesity, metabolic syndrome and esophageal adenocarcinoma: epidemiology, etiology and new targets. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011;35:309–319. - PubMed
-
- Ruigómez A, Wallander MA, Lundborg P, Johansson S, Rodriguez LA. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in children and adolescents in primary care. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:139–146. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Gilger M, Carter J, Genta RM, Rabeneck L. Childhood GERD is a risk factor for GERD in adolescents and young adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:806–812. - PubMed
-
- Nelson SP, Chen EH, Syniar GM, Christoffel KK. Prevalence of symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux during infancy. A pediatric practice-based survey. Pediatric Practice Research Group. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1997;151:569–572. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

