Antibody responses against influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus after sequential vaccination with pandemic and seasonal influenza vaccines in Finnish healthcare professionals
- PMID: 22913369
- PMCID: PMC5779819
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2012.00415.x
Antibody responses against influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus after sequential vaccination with pandemic and seasonal influenza vaccines in Finnish healthcare professionals
Abstract
Background: Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus has been circulating in human population for three epidemic seasons. During this time, monovalent pandemic and trivalent seasonal influenza vaccination against this virus have been offered to Finnish healthcare professionals. It is, however, unclear how well vaccine-induced antibodies recognize different strains of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 circulating in the population and whether the booster vaccination with seasonal influenza vaccine would broaden the antibody cross-reactivity.
Objectives: Influenza vaccine-induced humoral immunity against several isolates of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus was analyzed in healthcare professionals. Age-dependent responses were also analyzed.
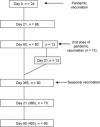
Methods: Influenza viruses were selected to represent viruses that circulated in Finland during two consecutive influenza epidemic seasons 2009-2010 and 2010-2011. Serum samples from vaccinated volunteers, age 20-64 years, were collected before and after vaccination with AS03-adjuvanted pandemic and non-adjuvanted trivalent seasonal influenza vaccine that was given 1 year later.
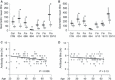
Results: Single dose of pandemic vaccine induced a good albeit variable antibody response. On day 21 after vaccination, depending on the virus strain, 14-75% of vaccinated had reached antibody titers (≥1:40) considered seroprotective. The booster vaccination 1 year later with a seasonal vaccine elevated the seroprotection rate to 57-98%. After primary immunization, younger individuals (20-48 years) had significantly higher antibody titers against all tested viruses than older persons (49-64 years) but this difference disappeared after the seasonal booster vaccination.
Conclusions: Even a few amino acid changes in influenza A HA may compromise the vaccine-induced antibody recognition. Older adults (49 years and older) may benefit more from repeated influenza vaccinations.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of pre-existing immunity on the induction of functional cross-reactive anti-hemagglutinin stalk antibodies following vaccination with an AS03 adjuvanted pandemic H1N1 vaccine.Vaccine. 2018 Apr 12;36(16):2213-2219. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.02.022. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 29548607
-
Seasonal influenza vaccines induced high levels of neutralizing cross-reactive antibody responses against different genetic group influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses.Vaccine. 2019 May 6;37(20):2731-2740. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.03.078. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 30954308
-
Single dose vaccination of the ASO3-adjuvanted A(H1N1)pdm09 monovalent vaccine in health care workers elicits homologous and cross-reactive cellular and humoral responses to H1N1 strains.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(7):1654-62. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1048939. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 26009966 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Influenza virus vaccines: lessons from the 2009 H1N1 pandemic.Curr Opin Virol. 2011 Oct;1(4):254-62. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.08.002. Curr Opin Virol. 2011. PMID: 22125588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pandemic influenza H1N1 2009, innate immunity, and the impact of immunosenescence on influenza vaccine.Yale J Biol Med. 2009 Dec;82(4):143-51. Yale J Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 20027279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Different Repeat Annual Influenza Vaccinations Improve the Antibody Response to Drifted Influenza Strains.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 12;7(1):5258. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05579-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28701762 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and Binding H1N1pdm09-Specific Antibody Responses in Occasionally and Repeatedly Vaccinated Healthcare Workers: A Five-Year Study (2009-2014).Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 6;12:748281. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.748281. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34938285 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antibody levels in a cohort of pregnant women after the 2009 influenza A(H1N1) pandemic: Waning and association with self-reported severity and duration of illness.Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2019 Mar;13(2):191-200. doi: 10.1111/irv.12623. Epub 2019 Jan 1. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30536590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roman F, Vaman T, Gerlach B, Markendorf A, Gillard P, Devaster JM. Immunogenicity and safety in adults of one dose of influenza A H1N1v 2009 vaccine formulated with and without AS03A‐adjuvant: preliminary report of an observer‐blind, randomised trial. Vaccine 2010; 28:1740–1745. - PubMed
-
- Roman F, Vaman T, Kafeja F, Hanon E, Van Damme P. AS03(A)‐Adjuvanted influenza A (H1N1) 2009 vaccine for adults up to 85 years of age. Clin Infect Dis 2010; 51:668–677. - PubMed
-
- Gilca V, De Serres G, Hamelin ME et al. Antibody persistence and response to 2010‐2011 trivalent influenza vaccine one year after a single dose of 2009 AS03‐adjuvanted pandemic H1N1 vaccine in children. Vaccine 2011; 30:35–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

