Production of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates by sequential feeding of xylose and octanoic acid in engineered Pseudomonas putida KT2440
- PMID: 22913372
- PMCID: PMC3542253
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-12-53
Production of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates by sequential feeding of xylose and octanoic acid in engineered Pseudomonas putida KT2440
Abstract
Background: Pseudomonas putida KT2440 is able to synthesize large amounts of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates (mcl-PHAs). To reduce the substrate cost, which represents nearly 50% of the total PHA production cost, xylose, a hemicellulose derivate, was tested as the growth carbon source in an engineered P. putida KT2440 strain.
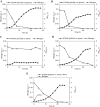
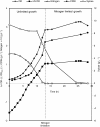
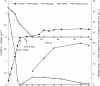
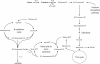
Results: The genes encoding xylose isomerase (XylA) and xylulokinase (XylB) from Escherichia coli W3110 were introduced into P. putida KT2440. The recombinant KT2440 exhibited a XylA activity of 1.47 U and a XylB activity of 0.97 U when grown on a defined medium supplemented with xylose. The cells reached a maximum specific growth rate of 0.24 h(-1) and a final cell dry weight (CDW) of 2.5 g L(-1) with a maximal yield of 0.5 g CDW g(-1) xylose. Since no mcl-PHA was accumulated from xylose, mcl-PHA production can be controlled by the addition of fatty acids leading to tailor-made PHA compositions. Sequential feeding strategy was applied using xylose as the growth substrate and octanoic acid as the precursor for mcl-PHA production. In this way, up to 20% w w(-1) of mcl-PHA was obtained. A yield of 0.37 g mcl-PHA per g octanoic acid was achieved under the employed conditions.
Conclusions: Sequential feeding of relatively cheap carbohydrates and expensive fatty acids is a practical way to achieve more cost-effective mcl-PHA production. This study is the first reported attempt to produce mcl-PHA by using xylose as the growth substrate. Further process optimizations to achieve higher cell density and higher productivity of mcl-PHA should be investigated. These scientific exercises will undoubtedly contribute to the economic feasibility of mcl-PHA production from renewable feedstock.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Review of the Developments of Bacterial Medium-Chain-Length Polyhydroxyalkanoates (mcl-PHAs).Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 May 21;9(5):225. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9050225. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35621503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering Pseudomonas putida S12 for efficient utilization of D-xylose and L-arabinose.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Aug;74(16):5031-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00924-08. Epub 2008 Jun 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18586973 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic engineering of genome-streamlined strain Pseudomonas putida KTU-U27 for medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate production from xylose and cellobiose.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Dec 31;253(Pt 2):126732. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126732. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37678685
-
Production of medium chain length polyhydroxyalkanoate from acetate by engineered Pseudomonas putida KT2440.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jun;46(6):793-800. doi: 10.1007/s10295-019-02159-5. Epub 2019 Mar 12. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30864026
-
Current trends in medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates: Microbial production, purification, and characterization.Eng Life Sci. 2024 Mar 7;24(6):2300211. doi: 10.1002/elsc.202300211. eCollection 2024 Jun. Eng Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38845815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of aromatic amino acids from 2G lignocellulosic substrates.Microb Biotechnol. 2021 Sep;14(5):1931-1943. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13844. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Microb Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34403199 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of fragrance 2-phenylethanol from sugars by Pseudomonas putida.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024 Apr 2;17(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02498-1. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024. PMID: 38566218 Free PMC article.
-
Development of genetic tools for heterologous protein expression in a pentose-utilizing environmental isolate of Pseudomonas putida.Microb Biotechnol. 2023 Mar;16(3):645-661. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14205. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Microb Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36691869 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the Developments of Bacterial Medium-Chain-Length Polyhydroxyalkanoates (mcl-PHAs).Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 May 21;9(5):225. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9050225. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35621503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization of a Two-Species Microbial Consortium for Improved Mcl-PHA Production From Glucose-Xylose Mixtures.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jan 10;9:794331. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.794331. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35083203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinbuchel A, Valentin HE. Diversity of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoic acids. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995;128(3):219–228.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

