Uniqueness, advantages, challenges, solutions, and perspectives in therapeutics applying RNA nanotechnology
- PMID: 22913595
- PMCID: PMC3426230
- DOI: 10.1089/nat.2012.0350
Uniqueness, advantages, challenges, solutions, and perspectives in therapeutics applying RNA nanotechnology
Abstract
The field of RNA nanotechnology is rapidly emerging. RNA can be manipulated with the simplicity characteristic of DNA to produce nanoparticles with a diversity of quaternary structures by self-assembly. Additionally RNA is tremendously versatile in its function and some RNA molecules display catalytic activities much like proteins. Thus, RNA has the advantage of both worlds. However, the instability of RNA has made many scientists flinch away from RNA nanotechnology. Other concerns that have deterred the progress of RNA therapeutics include the induction of interferons, stimulation of cytokines, and activation of other immune systems, as well as short pharmacokinetic profiles in vivo. This review will provide some solutions and perspectives on the chemical and thermodynamic stability, in vivo half-life and biodistribution, yield and production cost, in vivo toxicity and side effect, specific delivery and targeting, as well as endosomal trapping and escape.
Figures



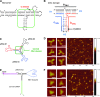
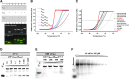

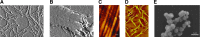
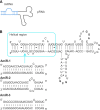

References
-
- BANTA S. MEGEED Z. CASALI M. REGE K. YARMUSH M.L. Engineering protein and peptide building blocks for nanotechnology. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007;7:387–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
