Reversal of cerebral radiation necrosis with bevacizumab treatment in 17 Chinese patients
- PMID: 22913802
- PMCID: PMC3493338
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783X-17-25
Reversal of cerebral radiation necrosis with bevacizumab treatment in 17 Chinese patients
Abstract
Background: Bevacizumab has been suggested as a new treatment modality for cerebral radiation necrosis due to its ability to block the effects of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in leakage-prone capillaries, though its use still remains controversial in clinical practice.
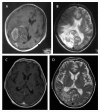
Methods: The use of bevacizumab in 17 patients with symptomatic cerebral radiation necrosis poorly controlled with dexamethasone steroid treatments was examined between March 2010 and January 2012. Bevacizumab therapy was administered for a minimum of two cycles (7.5 mg/kg, at two-week interval) with a median of four bevacizumab injections. Changes in bi-dimensional measurements of the largest radiation necrosis lesions were observed by gadolinium-enhanced and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Additionally, dexamethasone dosage, Karnofsky performance status (KPS), adverse event occurrence and associated clinical outcomes were recorded for each patient.
Results: MRI analysis revealed that the average reduction was 54.9% and 48.4% in post-gadolinium and T2-weighted sequence analysis, respectively. Significant clinical neurological improvements were expressed in 10 patients according to KPS values. Dexamethasone reduction was achieved four weeks after initiation of bevacizumab in all patients, with four patients successfully discontinuing dexamethasone treatment. Mild to moderate bevacizumab-related adverse events, such as fatigue, proteinuria and hypertension were observed in three patients. Upon follow-up at 4 to 12 months, 10 patients showed clinical improvement, and 7 patient deaths occurred from tumor progression (5 patients), recurrent necrosis (1 patient), and uncontrolled necrosis-induced edema (1 patient).
Conclusions: These findings suggest bevacizumab as a promising treatment for cerebral radiation necrosis induced by common radiation therapies, including external beam radiotherapy (EBRT), stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (FSRT).
Figures
References
-
- Ohguri T, Imada H, Kohshi K, Kakeda S, Ohnari N, Morioka T, Nakano K, Konda N, Korogi Y. Effect of prophylactic hyperbaric oxygen treatment for radiation-induced brain injury after stereotactic radiosurgery of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67:248–255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.08.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McPherson CM, Warnick RE. Results of contemporary surgical management of radiation necrosis using frameless stereotaxis and intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurooncol. 2004;68:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Levin VA, Bidaut L, Hou P, Kumar AJ, Wefel JS, Bekele BN, Prabhu S, Loghin M, Gilbert MR, Jackson EF. Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of bevacizumab therapy for radiation necrosis of the central nervous system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;79:1487–1495. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.12.061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

