Rate of de novo mutations and the importance of father's age to disease risk
- PMID: 22914163
- PMCID: PMC3548427
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11396
Rate of de novo mutations and the importance of father's age to disease risk
Abstract
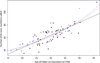
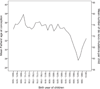
Mutations generate sequence diversity and provide a substrate for selection. The rate of de novo mutations is therefore of major importance to evolution. Here we conduct a study of genome-wide mutation rates by sequencing the entire genomes of 78 Icelandic parent-offspring trios at high coverage. We show that in our samples, with an average father's age of 29.7, the average de novo mutation rate is 1.20 × 10(-8) per nucleotide per generation. Most notably, the diversity in mutation rate of single nucleotide polymorphisms is dominated by the age of the father at conception of the child. The effect is an increase of about two mutations per year. An exponential model estimates paternal mutations doubling every 16.5 years. After accounting for random Poisson variation, father's age is estimated to explain nearly all of the remaining variation in the de novo mutation counts. These observations shed light on the importance of the father's age on the risk of diseases such as schizophrenia and autism.
Figures
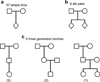
 proband schizophrenic;
proband schizophrenic;  proband a parent of an autistic case; □ others.
proband a parent of an autistic case; □ others.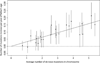
Comment in
-
Fathers bequeath more mutations as they age.Nature. 2012 Aug 23;488(7412):439. doi: 10.1038/488439a. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22914142 No abstract available.
-
Genetics: The rate of human mutation.Nature. 2012 Aug 23;488(7412):467-8. doi: 10.1038/488467a. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22914161 No abstract available.
-
Re: rate of De Novo mutations and the importance of father's age to disease risk.J Urol. 2013 Feb;189(2):655. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.10.098. Epub 2012 Oct 29. J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23312194 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

