A simple echocardiographic prediction rule for hemodynamics in pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 22914595
- PMCID: PMC3505751
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.112.976654
A simple echocardiographic prediction rule for hemodynamics in pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) has diverse causes with heterogeneous physiology compelling distinct management. Differentiating patients with primarily elevated pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) from those with PH predominantly because of elevated left-sided filling pressure is critical.
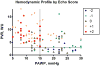
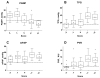
Methods and results: We reviewed hemodynamics, echocardiography, and clinical data for 108 patients seen at a referral PH clinic with transthoracic echocardiogram and right heart catheterization within 1 year. We derived a simple echocardiographic prediction rule to allow hemodynamic differentiation of PH attributed to pulmonary vascular disease (PH(PVD), defined as pulmonary artery wedge pressure [PAWP]≤15 mm Hg and PVR>3 WU). Age averaged 61.3±14.8 years, μPAWP and PVR were 16.4±7.1 mm Hg and 6.3±4.0 WU, respectively, and 52 (48.1%) patients fulfilled PH(PVD) hemodynamic criteria. The derived prediction rule ranged from -2 to +2 with higher scores suggesting higher probability of PH(PVD): +1 point for left atrial anterior-posterior dimension <3.2 cm; +1 for presence of a mid systolic notch or acceleration time <80 ms; -1 for lateral mitral E:e'>10; -1 for left atrial anterior-posterior dimension >4.2 cm. PVR increased stepwise with score (for -2, 0, and +2, μPVR were 2.5, 4.5, and 8.1 WU, respectively), whereas the inverse was true for pulmonary artery wedge pressure (corresponding μPAWP were 21.5, 16.5, and 10.4 mm Hg). Among subjects with complete data, the score had an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.921 for PH(PVD). A score ≥0 had 100% sensitivity and 69.3% positive predictive value for PH(PVD), with 62.3% specificity. No patients with a negative score had PH(PVD). Patients with a negative score and acceleration time >100 ms had normal PVR (μPVR=1.8 WU, range=0.7-3.2 WU).
Conclusions: We present a simple echocardiographic prediction rule that accurately defines PH hemodynamics, facilitates improved screening and focused clinical investigation for PH diagnosis and management.
Figures



References
-
- Galie N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA, Beghetti M, Corris P, Gaine S, Gibbs JS, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Jondeau G, Klepetko W, Opitz C, Peacock A, Rubin L, Zellweger M, Simonneau G. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2009;30:2493–2537. - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin VV, Presberg KW, Doyle RL, Abman SH, McCrory DC, Fortin T, Ahearn G. Prognosis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2004;126:78S–92S. - PubMed
-
- Rich JD, Shah SJ, Swamy RS, Kamp A, Rich S. Inaccuracy of Doppler echocardiographic estimates of pulmonary artery pressures in patients with pulmonary hypertension: implications for clinical practice. Chest. 2011;139:988–993. - PubMed
-
- Janda S, Shahidi N, Gin K, Swiston J. Diagnostic accuracy of echocardiography for pulmonary hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart. 2011;97:612–622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

