Tracking a hospital outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with whole-genome sequencing
- PMID: 22914622
- PMCID: PMC3521604
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004129
Tracking a hospital outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with whole-genome sequencing
Abstract
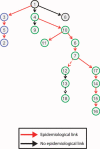
The Gram-negative bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae is a major cause of nosocomial infections, primarily among immunocompromised patients. The emergence of strains resistant to carbapenems has left few treatment options, making infection containment critical. In 2011, the U.S. National Institutes of Health Clinical Center experienced an outbreak of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae that affected 18 patients, 11 of whom died. Whole-genome sequencing was performed on K. pneumoniae isolates to gain insight into why the outbreak progressed despite early implementation of infection control procedures. Integrated genomic and epidemiological analysis traced the outbreak to three independent transmissions from a single patient who was discharged 3 weeks before the next case became clinically apparent. Additional genomic comparisons provided evidence for unexpected transmission routes, with subsequent mining of epidemiological data pointing to possible explanations for these transmissions. Our analysis demonstrates that integration of genomic and epidemiological data can yield actionable insights and facilitate the control of nosocomial transmission.
Figures



References
-
- Montgomerie JZ. Epidemiology of Klebsiella and hospital-associated infections. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1979;1:736–753. - PubMed
-
- Nordmann P, Cuzon G, Naas T. The real threat of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing bacteria. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009;9:228–236. - PubMed
-
- Gupta N, Limbago BM, Patel JB, Kallen AJ. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: epidemiology and prevention. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011;53:60–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

