Analysis and quantification of endovascular coil distribution inside saccular aneurysms using histological images
- PMID: 22914746
- PMCID: PMC3910323
- DOI: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2012-010456
Analysis and quantification of endovascular coil distribution inside saccular aneurysms using histological images
Abstract
Objective: Endovascular coiling is often performed by first placing coils along the aneurysm wall to create a frame and then by filling up the aneurysm core. However, little attention has been paid to quantifying this filling strategy and to see how it changes for different packing densities. The purpose of this work is to analyze and quantify endovascular coil distribution inside aneurysms based on serial histological images of experimental aneurysms.
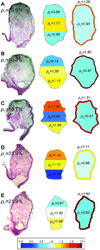
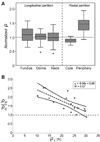
Method: Seventeen histological images from 10 elastase-induced saccular aneurysms in rabbits treated with coils were studied. In-slice coil density, defined as the area taken up by coil winds, was calculated on each histological image. Images were analyzed by partitioning the aneurysm along its longitudinal and radial axes. Coil distribution was quantified by measuring and comparing the in-slice coil density of each partition.
Results: Mean total in-slice coil density was 22.0 ± 6.2% (range 10.1-30.2%). The density was non-significantly different (p = 0.465) along the longitudinal axis. A significant difference (p < 0.001) between peripheral and core densities was found. Additionally, the peripheral-core density ratio was observed to be inversely proportional to the total in-slice coil density (R(2)=0.57, p <0.001). This ratio was near unity for high in-slice coil density (around 30%).
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate and confirm that coils tend to be located near the aneurysm periphery when few are inserted. However, when more coils are added, the radial distribution becomes more homogeneous. Coils are homogeneously distributed along the longitudinal axis.
Keywords: Aneurysm; Coil; Technique.
Figures

References
-
- Pruvo JP, Leclerc X, Ares GS, Lejeune JP, Leys D. Endovascular treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Neurol. 1999;246(4):244–249. - PubMed
-
- Vallee JN, Pierot L, Mont'alverne F, et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms treated by three-dimensional coil embolization: evaluation of the postoperative aneurysm occlusion volume. Neuroradiology. 2005;47(6):438–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
