HOXB7 promotes invasion and predicts survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 22914903
- PMCID: PMC3867310
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.27725
HOXB7 promotes invasion and predicts survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: The homeobox gene HOXB7 is overexpressed across a range of cancers and promotes tumorigenesis through varying effects on proliferation, survival, invasion, and angiogenesis. Although published microarray data suggest HOXB7 is overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), its function in pancreatic cancer has not been studied.
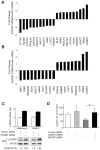
Methods: HOXB7 message and protein levels were examined in PDAC cell lines and patient samples, as well as in normal pancreas. HOXB7 protein expression in patient tumors was determined by immunohistochemistry and correlated with clinicopathologic factors and survival. The impact of HOXB7 on cell proliferation, growth, and invasion was assessed by knockdown and overexpression in PDAC cell lines. Candidate genes whose expression levels were altered following HOXB7 knockdown were determined by microarray analysis.
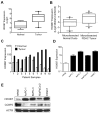
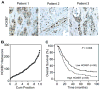
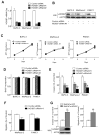
Results: HOXB7 message and protein levels were significantly elevated in PDAC cell lines and patient tumor samples relative to normal pancreas. Evaluation of a tissue microarray of 145 resected PDACs found high HOXB7 protein expression was correlated with lymph node metastasis (P = .034) and an independent predictor of worse overall survival in multivariate analysis (hazard ratio = 1.56, 95% confidence interval = 1.02-2.39). HOXB7 knockdown or overexpression in PDAC cell lines resulted in decreased or increased invasion, respectively, without influencing proliferation or cell viability.
Conclusions: HOXB7 is frequently overexpressed in PDAC, specifically promotes invasive phenotype, and is associated with lymph node metastasis and worse survival outcome. HOXB7 and its downstream targets may represent novel clinical biomarkers or targets of therapy for inhibiting the invasive and metastatic capacity of PDAC.
Copyright © 2012 American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE
The authors made no disclosure.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2010. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2010.
-
- Stathis A, Moore MJ. Advanced pancreatic carcinoma: current treatment and future challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010;7:163–172. - PubMed
-
- Neoptolemos JP, Stocken DD, Bassi C, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy with fluorouracil plus folinic acid vs gemcitabine following pancreatic cancer resection: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2010;304:1073–1081. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Mihaljevic AL, Michalski CW, Friess H, Kleeff J. Molecular mechanism of pancreatic cancer--understanding proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2010;395:295–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

