Role of resting metabolic rate and energy expenditure in hunger and appetite control: a new formulation
- PMID: 22915022
- PMCID: PMC3424457
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.009837
Role of resting metabolic rate and energy expenditure in hunger and appetite control: a new formulation
Abstract
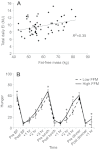
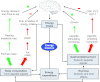
A long-running issue in appetite research concerns the influence of energy expenditure on energy intake. More than 50 years ago, Otto G. Edholm proposed that "the differences between the intakes of food [of individuals] must originate in differences in the expenditure of energy". However, a relationship between energy expenditure and energy intake within any one day could not be found, although there was a correlation over 2 weeks. This issue was never resolved before interest in integrative biology was replaced by molecular biochemistry. Using a psychobiological approach, we have studied appetite control in an energy balance framework using a multi-level experimental system on a single cohort of overweight and obese human subjects. This has disclosed relationships between variables in the domains of body composition [fat-free mass (FFM), fat mass (FM)], metabolism, gastrointestinal hormones, hunger and energy intake. In this Commentary, we review our own and other data, and discuss a new formulation whereby appetite control and energy intake are regulated by energy expenditure. Specifically, we propose that FFM (the largest contributor to resting metabolic rate), but not body mass index or FM, is closely associated with self-determined meal size and daily energy intake. This formulation has implications for understanding weight regulation and the management of obesity.
Figures
References
-
- Badman M. K., Flier J. S. (2005). The gut and energy balance: visceral allies in the obesity wars. Science 307, 1909–1914 - PubMed
-
- Blundell J. E., Macdiarmid J. I. (1997). Passive overconsumption. Fat intake and short-term energy balance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 827, 392–407 - PubMed
-
- Blundell J. E., King N. A. (1998). Effects of exercise on appetite control: loose coupling between energy expenditure and energy intake. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 22 Suppl. 2, S22–S29 - PubMed
-
- Blundell J. E., Caudwell P., Gibbons C., Hopkins M., Näslund E., King N. A., Finlayson G. (2012). Body composition and appetite: fat-free mass (but not fat mass or BMI) is positively associated with self-determined meal size and daily energy intake in humans. Br. J. Nutr. 107, 445–449 - PubMed
-
- Broom D. R., Stensel D. J., Bishop N. C., Burns S. F., Miyashita M. (2007). Exercise-induced suppression of acylated ghrelin in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 102, 2165–2171 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

