Arf6-GEF BRAG1 regulates JNK-mediated synaptic removal of GluA1-containing AMPA receptors: a new mechanism for nonsyndromic X-linked mental disorder
- PMID: 22915114
- PMCID: PMC3459061
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1942-12.2012
Arf6-GEF BRAG1 regulates JNK-mediated synaptic removal of GluA1-containing AMPA receptors: a new mechanism for nonsyndromic X-linked mental disorder
Abstract
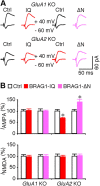
Activity-dependent modifications of excitatory synapses contribute to synaptic maturation and plasticity, and are critical for learning and memory. Consequently, impairments in synapse formation or synaptic transmission are thought to be responsible for several types of mental disabilities. BRAG1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the small GTP-binding protein Arf6 that localizes to the postsynaptic density of excitatory synapses. Mutations in BRAG1 have been identified in families with X-linked intellectual disability (XLID). These mutations mapped to either the catalytic domain or an IQ-like motif; however, the pathophysiological basis of these mutations remains unknown. Here, we show that the BRAG1 IQ motif binds apo-calmodulin (CaM), and that calcium-induced CaM release triggers a reversible conformational change in human BRAG1. We demonstrate that BRAG1 activity, stimulated by activation of NMDA-sensitive glutamate receptors, depresses AMPA receptor (AMPA-R)-mediated transmission via JNK-mediated synaptic removal of GluA1-containing AMPA-Rs in rat hippocampal neurons. Importantly, a BRAG1 mutant that fails to activate Arf6 also fails to depress AMPA-R signaling, indicating that Arf6 activity is necessary for this process. Conversely, a mutation in the BRAG1 IQ-like motif that impairs CaM binding results in hyperactivation of Arf6 signaling and constitutive depression of AMPA transmission. Our findings reveal a role for BRAG1 in response to neuronal activity with possible clinical relevance to nonsyndromic XLID.
Figures





Similar articles
-
BRAG1/IQSEC2 as a regulator of small GTPase-dependent trafficking.Small GTPases. 2020 Jan;11(1):1-7. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1361898. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Small GTPases. 2020. PMID: 29363391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subunit-selective N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Signaling through Brefeldin A-resistant Arf Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors BRAG1 and BRAG2 during Synapse Maturation.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 22;291(17):9105-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.691717. Epub 2016 Feb 16. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26884337 Free PMC article.
-
IQ-ArfGEF/BRAG1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Arf6 that interacts with PSD-95 at postsynaptic density of excitatory synapses.Neurosci Res. 2008 Feb;60(2):199-212. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2007.10.013. Epub 2007 Nov 17. Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18164504
-
Rap2-JNK removes synaptic AMPA receptors during depotentiation.Neuron. 2005 Jun 16;46(6):905-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.04.037. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 15953419
-
Synaptic Signaling in Learning and Memory.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Dec 30;8(2):a016824. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016824. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 24379319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The BRAG/IQSec family of Arf GEFs.Small GTPases. 2016 Oct;7(4):257-264. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1219442. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Small GTPases. 2016. PMID: 27739918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The small GTPase ARF6 regulates GABAergic synapse development.Mol Brain. 2020 Jan 6;13(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13041-019-0543-3. Mol Brain. 2020. PMID: 31907062 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and Pathological Roles of the Cytohesin Family in Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 3;23(9):5087. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095087. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and Functional Analysis of the Human IQSEC2 S1474Qfs*133 Mutation.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 29;15(5):635. doi: 10.3390/biom15050635. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40427528 Free PMC article.
-
BRAG1/IQSEC2 as a regulator of small GTPase-dependent trafficking.Small GTPases. 2020 Jan;11(1):1-7. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1361898. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Small GTPases. 2020. PMID: 29363391 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Billuart P, Bienvenu T, Ronce N, des Portes V, Vinet MC, Zemni R, Roest Crollius H, Carri é A, Fauchereau F, Cherry M, Briault S, Hamel B, Fryns JP, Beldjord C, Kahn A, Moraine C, Chelly J. Oligophrenin-1 encodes a rhoGAP protein involved in X-linked mental retardation. Nature. 1998;392:923–926. - PubMed
-
- Bolshakov VY, Carboni L, Cobb MH, Siegelbaum SA, Belardetti F. Dual MAP kinase pathways mediate opposing forms of long-term plasticity at CA3-CA1 synapses. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:1107–1112. - PubMed
-
- Burkhard P, Stetefeld J, Strelkov SV. Coiled coils: a highly versatile protein folding motif. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:82–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
