Sitagliptin reduces hyperglycemia and increases satiety hormone secretion more effectively when used with a novel polysaccharide in obese Zucker rats
- PMID: 22915295
- PMCID: PMC3718709
- DOI: 10.3945/jn.112.163204
Sitagliptin reduces hyperglycemia and increases satiety hormone secretion more effectively when used with a novel polysaccharide in obese Zucker rats
Abstract
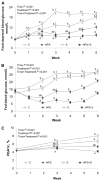
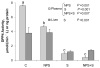
The novel polysaccharide (NPS) PolyGlycopleX (PGX) has been shown to reduce glycemia. Pharmacological treatment with sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitor, also reduces glycemia by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). Our objective was to determine if using NPS in combination with sitagliptin reduces hyperglycemia in Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats more so than either treatment alone. Male ZDF rats were randomized to: 1) cellulose/vehicle [control (C)]; 2) NPS (5% wt:wt)/vehicle (NPS); 3) cellulose/sitagliptin [10 mg/(kg · d) (S)]; or 4) NPS (5%) + S [10 mg/(kg · d) (NPS+S)]. Glucose tolerance, adiposity, satiety hormones, and mechanisms related to DPP4 activity and hepatic and pancreatic histology were examined. A clinically relevant reduction in hyperglycemia occurred in the rats treated with NPS+S (P = 0.001) compared with NPS and S alone. Blood glucose, measured weekly in fed and feed-deprived rats and during an oral glucose tolerance test, was lower in the NPS+S group compared with all other groups (all P = 0.001). At wk 6, glycated hemoglobin was lower in the NPS+S group than in the C and S (P = 0.001) and NPS (P = 0.06) groups. PGX (P = 0.001) and S (P = 0.014) contributed to increased lean mass. Active GLP-1 was increased by S (P = 0.001) and GIP was increased by NPS (P = 0.001). Plasma DPP4 activity was lower in the NPS+S and S groups than in the NPS and C groups (P = 0.007). Insulin secretion and β-cell mass was increased with NPS (P < 0.05). NPS alone reduced LDL cholesterol and hepatic steatosis (P < 0.01). Independently, NPS and S improve several metabolic outcomes in ZDF rats, but combined, their ability to markedly reduce glycemia suggests they may be a promising dietary/pharmacological co-therapy for type 2 diabetes management.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combining sitagliptin/metformin with a functional fiber delays diabetes progression in Zucker rats.J Endocrinol. 2014 Feb 10;220(3):361-73. doi: 10.1530/JOE-13-0484. Print 2014 Mar. J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24389593
-
Effects of the soluble fiber complex PolyGlycopleX® (PGX®) on glycemic control, insulin secretion, and GLP-1 levels in Zucker diabetic rats.Life Sci. 2011 Feb 28;88(9-10):392-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.11.014. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21115020
-
Restoration of the insulinotropic effect of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide contributes to the antidiabetic effect of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015 Jan;17(1):74-81. doi: 10.1111/dom.12395. Epub 2014 Oct 26. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015. PMID: 25243647 Clinical Trial.
-
Sitagliptin: profile of a novel DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (update).Drugs Today (Barc). 2007 Nov;43(11):801-14. doi: 10.1358/dot.2007.43.11.1157620. Drugs Today (Barc). 2007. PMID: 18174966 Review.
-
Sitagliptin: Profile of a novel DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Drugs Today (Barc). 2007 Jan;43(1):13-25. doi: 10.1358/dot.2007.43.1.1043909. Drugs Today (Barc). 2007. PMID: 17315049 Review.
Cited by
-
Daily supplementation of dietary protein improves the metabolic effects of GLP-1-based pharmacotherapy in lean and obese rats.Physiol Behav. 2017 Aug 1;177:122-128. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.04.017. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Physiol Behav. 2017. PMID: 28433470 Free PMC article.
-
A novel combination of sitagliptin and melatonin ameliorates T2D manifestations: studies on experimental diabetic models.J Endocrinol Invest. 2023 Aug;46(8):1597-1612. doi: 10.1007/s40618-023-02014-6. Epub 2023 Jan 24. J Endocrinol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36692817
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, diet and gut microbiota.EXCLI J. 2014 May 7;13:461-90. eCollection 2014. EXCLI J. 2014. Retraction in: EXCLI J. 2017 Oct 18;16:1164. PMID: 26417275 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Safety of alginate-konjac-xanthan polysaccharide complex (PGX) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 258/97.EFSA J. 2017 May 8;15(5):e04776. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4776. eCollection 2017 May. EFSA J. 2017. PMID: 32625482 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a functional fibre supplement on glycemic control when added to a year-long medically supervised weight management program in adults with type 2 diabetes.Eur J Nutr. 2021 Apr;60(3):1237-1251. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02328-8. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Eur J Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32642971 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Fincham JE. The expanding public health threat of obesity and overweight. Int J Pharm Pract. 2011;19:214–6. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Fact sheet no 311. WHO Media Centre; 2011. Obesity and overweight. [cited 2011 Nov]. Available from: www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/index.html.
-
- NIH. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults. The evidence report. Obes Res. 1998;6(Suppl 2):S51–209. - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: clinical data and clinical implications. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:1344–50. - PubMed
-
- Baggio LL, Drucker DJ. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2131–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

