High-resolution MRI of early-stage mouse embryos
- PMID: 22915475
- PMCID: PMC3524402
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.2843
High-resolution MRI of early-stage mouse embryos
Abstract
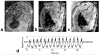
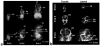
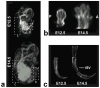
Both the availability of methods to manipulate genes and the completion of the mouse genome sequence have led to the generation of thousands of genetically modified mouse lines that provide a new platform for the study of mammalian development and developmental diseases. Phenotyping of mouse embryos has traditionally been performed on fixed embryos by the use of ex vivo histological, optical and high-resolution MRI techniques. Although potentially powerful, longitudinal imaging of individual animals is difficult or impossible with conventional optical methods because of the inaccessibility of mouse embryos inside the maternal uterus. To address this problem, we present a method of imaging the mouse embryo from stages as early as embryonic day (E)10.5, close to the onset of organogenesis in most physiological systems. This method uses a self-gated MRI protocol, combined with image registration, to obtain whole-embryo high-resolution (100 µm isotropic) three-dimensional images. Using this approach, we demonstrate high contrast in the cerebral vasculature, limbs, spine and central nervous system without the use of contrast agents. These results indicate the potential of MRI for the longitudinal imaging of developing mouse embryos in utero and for future applications in analyzing mutant mouse phenotypes.
Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In utero phenotyping of mouse embryonic vasculature with MRI.Magn Reson Med. 2012 Jan;67(1):251-7. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22991. Epub 2011 May 16. Magn Reson Med. 2012. PMID: 21590728 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional, in vivo MRI with self-gating and image coregistration in the mouse.Magn Reson Med. 2009 May;61(5):1148-57. doi: 10.1002/mrm.21945. Magn Reson Med. 2009. PMID: 19253389 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced tissue differentiation in the developing mouse brain using magnetic resonance micro-histology.Magn Reson Med. 2013 Nov;70(5):1380-8. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24573. Epub 2012 Dec 4. Magn Reson Med. 2013. PMID: 23213043
-
Magnetic resonance imaging of embryonic and fetal development in model systems.Methods Mol Med. 2006;124:87-101. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-010-3:87. Methods Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16506418 Review.
-
Mouse morphological phenotyping with magnetic resonance imaging.Methods Mol Med. 2006;124:103-27. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-010-3:103. Methods Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16506419 Review.
Cited by
-
3D mapping of neuronal migration in the embryonic mouse brain with magnetic resonance microimaging.Neuroimage. 2015 Jul 1;114:303-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.04.010. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Neuroimage. 2015. PMID: 25869862 Free PMC article.
-
QUEST MRI assessment of fetal brain oxidative stress in utero.Neuroimage. 2019 Oct 15;200:601-606. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.05.069. Epub 2019 May 31. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 31158477 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive Tracking of Embryonic Cardiac Dynamics and Development with Volumetric Optoacoustic Spectroscopy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jun;11(22):e2400089. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400089. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38526147 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse embryo phenotyping with optical coherence tomography.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 9;10:1000237. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1000237. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36158219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular Imaging in Mice.Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2016 Mar 1;6(1):15-38. doi: 10.1002/9780470942390.mo150122. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2016. PMID: 26928662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Waterston RH, Lindblad-Toh K, Birney E, Rogers J, Abril JF, Agarwal P, Agarwala R, Ainscough R, Alexandersson M, An P, Antonarakis SE, Attwood J, Baertsch R, Bailey J, Barlow K, Beck S, Berry E, Birren B, Bloom T, Bork P, Botcherby M, Bray N, Brent MR, Brown DG, Brown SD, Bult C, Burton J, Butler J, Campbell RD, Carninci P, Cawley S, Chiaromonte F, Chinwalla AT, Church DM, Clamp M, Clee C, Collins FS, Cook LL, Copley RR, Coulson A, Couronne O, Cuff J, Curwen V, Cutts T, Daly M, David R, Davies J, Delehaunty KD, Deri J, Dermitzakis ET, Dewey C, Dickens NJ, Diekhans M, Dodge S, Dubchak I, Dunn DM, Eddy SR, Elnitski L, Emes RD, Eswara P, Eyras E, Felsenfeld A, Fewell GA, Flicek P, Foley K, Frankel WN, Fulton LA, Fulton RS, Furey TS, Gage D, Gibbs RA, Glusman G, Gnerre S, Goldman N, Goodstadt L, Grafham D, Graves TA, Green ED, Gregory S, Guigo R, Guyer M, Hardison RC, Haussler D, Hayashizaki Y, Hillier LW, Hinrichs A, Hlavina W, Holzer T, Hsu F, Hua A, Hubbard T, Hunt A, Jackson I, Jaffe DB, Johnson LS, Jones M, Jones TA, Joy A, Kamal M, Karlsson EK, Karolchik D, Kasprzyk A, Kawai J, Keibler E, Kells C, Kent WJ, Kirby A, Kolbe DL, Korf I, Kucherlapati RS, Kulbokas EJ, Kulp D, Landers T, Leger JP, Leonard S, Letunic I, Levine R, Li J, Li M, Lloyd C, Lucas S, Ma B, Maglott DR, Mardis ER, Matthews L, Mauceli E, Mayer JH, McCarthy M, McCombie WR, McLaren S, McLay K, McPherson JD, Meldrim J, Meredith B, Mesirov JP, Miller W, Miner TL, Mongin E, Montgomery KT, Morgan M, Mott R, Mullikin JC, Muzny DM, Nash WE, Nelson JO, Nhan MN, Nicol R, Ning Z, Nusbaum C, O’Connor MJ, Okazaki Y, Oliver K, Larty EO, Pachter L, Parra G, Pepin KH, Peterson J, Pevzner P, Plumb R, Pohl CS, Poliakov A, Ponce TC, Ponting CP, Potter S, Quail M, Reymond A, Roe BA, Roskin KM, Rubin EM, Rust AG, Santos R, Sapojnikov V, Schultz B, Schultz J, Schwartz MS, Schwartz S, Scott C, Seaman S, Searle S, Sharpe T, Sheridan A, Shownkeen R, Sims S, Singer JB, Slater G, Smit A, Smith DR, Spencer B, Stabenau A, Strange-Thomann NS, Sugnet C, Suyama M, Tesler G, Thompson J, Torrents D, Trevaskis E, Tromp J, Ucla C, Vidal AU, Vinson JP, von Niederhausern AC, Wade CM, Wall M, Weber RJ, Weiss RB, Wendl MC, West AP, Wetterstrand K, Wheeler R, Whelan S, Wierzbowski J, Willey D, Williams S, Wilson RK, Winter E, Worley KC, Wyman D, Yang S, Yang SP, Zdobnov EM, Zody MC, Lander ES Mouse Genome Sequencing C. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature. 2002;420(6915):520–562. - PubMed
-
- Collins FS Int Mouse Knockout C. A mouse for all reasons. Cell. 2007;128(1):9–13. - PubMed
-
- Nieman BJ, Wong MD, Henkelman RM. Genes into geometry: imaging for mouse development in 3D. Curr Opin Genetics Dev. 2011;21(5):638–646. - PubMed
-
- Henkelman RM. Systems biology through mouse imaging centers: Experience and new directions. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2010;12:143–166. - PubMed
-
- Kaufman MH. The atlas of mouse development. London: Academic Press; 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

