Nanoparticle-based delivery of small interfering RNA: challenges for cancer therapy
- PMID: 22915840
- PMCID: PMC3418108
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S23696
Nanoparticle-based delivery of small interfering RNA: challenges for cancer therapy
Abstract
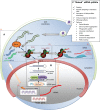
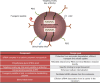
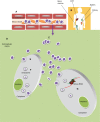
During recent decades there have been remarkable advances and profound changes in cancer therapy. Many therapeutic strategies learned at the bench, including monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors, have been used at the bedside, leading to important successes. One of the most important advances in biology has been the discovery that small interfering RNA (siRNA) is able to regulate the expression of genes, by a phenomenon known as RNA interference (RNAi). RNAi is one of the most rapidly growing fields of research in biology and therapeutics. Much research effort has gone into the application of this new discovery in the treatment of various diseases, including cancer. However, even though these molecules may have potential and strong utility, some limitations make their clinical application difficult, including delivery problems, side effects due to off-target actions, disturbance of physiological functions of the cellular machinery involved in gene silencing, and induction of the innate immune response. Many researchers have attempted to overcome these limitations and to improve the safety of potential RNAi-based therapeutics. Nanoparticles, which are nanostructured entities with tunable size, shape, and surface, as well as biological behavior, provide an ideal opportunity to modify current treatment regimens in a substantial way. These nanoparticles could be designed to surmount one or more of the barriers encountered by siRNA. Nanoparticle drug formulations afford the chance to improve drug bioavailability, exploiting superior tissue permeability, payload protection, and the "stealth" features of these entities. The main aims of this review are: to explain the siRNA mechanism with regard to potential applications in siRNA-based cancer therapy; to discuss the possible usefulness of nanoparticle-based delivery of certain molecules for overcoming present therapeutic limitations; to review the ongoing relevant clinical research with its pitfalls and promises; and to evaluate critically future perspectives and challenges in siRNA-based cancer therapy.
Keywords: biological barriers; cancer therapy; clinical trials; delivery strategies; nanoparticles; small interfering RNA.
Figures
References
-
- Druker B, Guilhot F, O’Brian S, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–2417. - PubMed
-
- Goldenberg MM. Trastuzumab, a recombinant DNA derived humanized monoclonal antibody, a novel agent for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Clin Ther. 1999;2:309–318. - PubMed
-
- Peterson C. Drug therapy of cancer. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;67:437–447. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert W. The RNA world. Nature. 1986;319:216.
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

