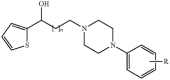
A Novel Carbamoyloxy Arylalkanoyl Arylpiperazine Compound (SKL-NP) Inhibits Hyperpolarization-Activated Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated (HCN) Channel Currents in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
- PMID: 22915988
- PMCID: PMC3419758
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.4.237
A Novel Carbamoyloxy Arylalkanoyl Arylpiperazine Compound (SKL-NP) Inhibits Hyperpolarization-Activated Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated (HCN) Channel Currents in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
Retraction in
-
Retraction: A Novel Carbamoyloxy Arylalkanoyl Arylpiperazine Compound (SKL-NP) Inhibits Hyperpolarization-Activated Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated (HCN) Channel Currents in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 Oct;16(5):367. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.5.367. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23118563 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
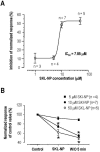
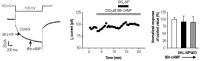
In this study, we determined mode of action of a novel carbamoyloxy arylalkanoyl arylpiperazine compound (SKL-NP) on hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel currents (I(h)) that plays important roles in neuropathic pain. In small or medium-sized dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons (<40 µm in diameter) exhibiting tonic firing and prominent I(h), SKL-NP inhibited I(h) and spike firings in a concentration dependent manner (IC(50)=7.85 µM). SKL-NP-induced inhibition of I(h) was blocked by pretreatment of pertussis toxin (PTX) and N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) as well as 8-Br-cAMP, a membrane permeable cAMP analogue. These results suggest that SKL-NP modulates I(h) in indirect manner by the activation of a Gi-protein coupled receptor that decreases intracellular cAMP concentration. Taken together, SKL-NP has the inhibitory effect on HCN channel currents (I(h)) in DRG neurons of rats.
Keywords: Gi-protein; Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel; Ih; Neuropathic pain; cAMP.
Figures


References
-
- Wickenden AD, Maher MP, Chaplan SR. HCN pacemaker channels and pain: a drug discovery perspective. Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15:2149–2168. - PubMed
-
- Yeon KY, Chung G, Kim YH, Hwang JH, Davies AJ, Park MK, Ahn DK, Kim JS, Jung SJ, Oh SB. Eugenol reverses mechanical allodynia after peripheral nerve injury by inhibiting hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels. Pain. 2011;152:2108–2116. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

