Luteolin induces microRNA-132 expression and modulates neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells
- PMID: 22916239
- PMCID: PMC3420912
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043304
Luteolin induces microRNA-132 expression and modulates neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells
Abstract
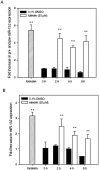
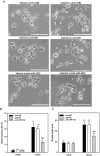
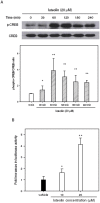
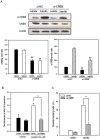
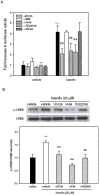
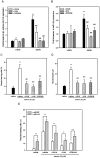
Luteolin (3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone), a food-derived flavonoid, has been reported to exert neurotrophic properties that are associated with its capacity to promote neuronal survival and neurite outgrowth. In this study, we report for the first time that luteolin induces the persistent expression of microRNA-132 (miR-132) in PC12 cells. The correlation between miR-132 knockdown and a decrease in luteolin-mediated neurite outgrowth may indicate a mechanistic link by which miR-132 functions as a mediator for neuritogenesis. Furthermore, we find that luteolin led to the phosphorylation and activation of cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), which is associated with the up-regulation of miR-132 and neurite outgrowth. Moreover, luteolin-induced CREB activation, miR-132 expression and neurite outgrowth were inhibited by adenylate cyclase, protein kinase A (PKA) and MAPK/ERK kinase 1/2 (MEK1/2) inhibitors but not by protein kinase C (PKC) or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMK II) inhibitors. Consistently, we find that luteolin treatment increases ERK phosphorylation and PKA activity in PC12 cells. These results show that luteolin induces the up-regulation of miR-132, which serves as an important regulator for neurotrophic actions, mainly acting through the activation of cAMP/PKA- and ERK-dependent CREB signaling pathways in PC12 cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Ambros V (2008) The evolution of our thinking about microRNAs. Nat Med 14: 1036–1040. - PubMed
-
- Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, et al. (2005) Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 433: 769–773. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

