S-nitrosoglutathione acts as a small molecule modulator of human fibrin clot architecture
- PMID: 22916291
- PMCID: PMC3423378
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043660
S-nitrosoglutathione acts as a small molecule modulator of human fibrin clot architecture
Abstract
Background: Altered fibrin clot architecture is increasingly associated with cardiovascular diseases; yet, little is known about how fibrin networks are affected by small molecules that alter fibrinogen structure. Based on previous evidence that S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) alters fibrinogen secondary structure and fibrin polymerization kinetics, we hypothesized that GSNO would alter fibrin microstructure.
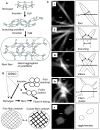
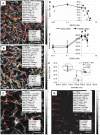
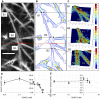
Methodology/principal findings: Accordingly, we treated human platelet-poor plasma with GSNO (0.01-3.75 mM) and imaged thrombin induced fibrin networks using multiphoton microscopy. Using custom designed computer software, we analyzed fibrin microstructure for changes in structural features including fiber density, diameter, branch point density, crossing fibers and void area. We report for the first time that GSNO dose-dependently decreased fibrin density until complete network inhibition was achieved. At low dose GSNO, fiber diameter increased 25%, maintaining clot void volume at approximately 70%. However, at high dose GSNO, abnormal irregularly shaped fibrin clusters with high fluorescence intensity cores were detected and clot void volume increased dramatically. Notwithstanding fibrin clusters, the clot remained stable, as fiber branching was insensitive to GSNO and there was no evidence of fiber motion within the network. Moreover, at the highest GSNO dose tested, we observed for the first time, that GSNO induced formation of fibrin agglomerates.
Conclusions/significance: Taken together, low dose GSNO modulated fibrin microstructure generating coarse fibrin networks with thicker fibers; however, higher doses of GSNO induced abnormal fibrin structures and fibrin agglomerates. Since GSNO maintained clot void volume, while altering fiber diameter it suggests that GSNO may modulate the remodeling or inhibition of fibrin networks over an optimal concentration range.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Collet JP, Allali Y, Lesty C, Tanguy ML, Silvain J, et al. (2006) Altered fibrin architecture is associated with hypofibrinolysis and premature coronary atherothrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26: 2567–2573. - PubMed
-
- Mills JD, Ariens RA, Mansfield MW, Grant PJ (2002) Altered fibrin clot structure in the healthy relatives of patients with premature coronary artery disease. Circulation 106: 1938–1942. - PubMed
-
- Scott DJ, Prasad P, Philippou H, Rashid ST, Sohrabi S, et al. (2011) Clot architecture is altered in abdominal aortic aneurysms and correlates with aneurysm size. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31: 3004–3010. - PubMed
-
- Undas A, Podolec P, Zawilska K, Pieculewicz M, Jedlinski I, et al. (2009) Altered fibrin clot structure/function in patients with cryptogenic ischemic stroke. Stroke 40: 1499–1501. - PubMed
-
- Vadseth C, Souza JM, Thomson L, Seagraves A, Nagaswami C, et al. (2004) Pro-thrombotic state induced by post-translational modification of fibrinogen by reactive nitrogen species. J Biol Chem 279: 8820–8826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

