Effect of add-on direct renin inhibitor aliskiren in patients with non-diabetes related chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 22917002
- PMCID: PMC3509390
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-13-89
Effect of add-on direct renin inhibitor aliskiren in patients with non-diabetes related chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) plays an important role in the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Although dual RAAS inhibition results in worse renal outcomes than monotherapy in high risk type 2 diabetes patients, the effect of dual RAAS inhibition in patients with non-DM CKD is unclear. The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential renoprotective effect of add-on direct renin inhibitor in non-DM CKD patients.
Methods: We retrospectively enrolled 189 non-DM CKD patients who had been taking angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) for more than six months. Patients were divided into an add-on aliskiren group and an ARB monotherapy group. The primary outcomes were a decline in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and a reduction in urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio at six months.
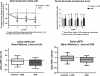
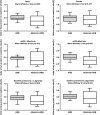
Results: The baseline characteristics of the two groups were similar. Aliskiren 150 mg daily reduced the urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio by 26% (95% confidence interval, 15 to 37%; p < 0.001). The decline in GFR was smaller in the add-on aliskiren group (-2.1 vs. -4.0 ml/min, p = 0.038). Add-on aliskiren had a neutral effect on serum potassium in the non-DM CKD patients. In subgroup analysis, the proteinuria-reducing effect of aliskiren was more prominent in patients with a GFR less than 60 ml/min, and in patients with a urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio greater than 1.8. The effect of aliskiren in retarding the decline in GFR was more prominent in patients with hypertensive nephropathy than in those with glomerulonephritis.
Conclusion: Add-on direct renin inhibitor aliskiren (150 mg daily) safely reduced proteinuria and attenuated the decline in GFR in the non-DM CKD patients who were receiving ARBs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dual RAAS Blockade with Aliskiren in Patients with Severely Impaired Chronic Kidney Disease.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2018 Jan;126(1):39-52. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-106440. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 28449154
-
Aliskiren add-on therapy effectively reduces proteinuria in chronic kidney disease: an open-label prospective trial.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2014 Sep;15(3):271-7. doi: 10.1177/1470320312467560. Epub 2012 Dec 7. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2014. PMID: 23223162 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy analysis of the renoprotective effects of aliskiren in hypertensive patients with chronic kidney disease.Heart Vessels. 2013 Jul;28(4):442-52. doi: 10.1007/s00380-012-0260-7. Epub 2012 May 23. Heart Vessels. 2013. PMID: 22618635 Clinical Trial.
-
[Direct renin inhibitor aliskiren in the treatment of cardiovascular and renal diseases].Vnitr Lek. 2010 Feb;56(2):120-6. Vnitr Lek. 2010. PMID: 20329582 Review. Czech.
-
Direct renin inhibition in chronic kidney disease.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;76(4):580-6. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12072. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23278708 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of aliskiren, compared with angiotensin II blockade, in slowing the progression of diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice: should the combination therapy be a focus?Am J Transl Res. 2015 May 15;7(5):825-40. eCollection 2015. Am J Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 26175845 Free PMC article.
-
Direct inhibition of plasmatic renin activity with aliskiren: a promising but under-investigated therapeutic option for non-diabetic glomerulonephritis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2016 Feb;48(2):229-37. doi: 10.1007/s11255-015-1128-4. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26438325 Review.
-
Successful long-term effects of direct renin inhibitor aliskiren in a patient with atherosclerotic renovascular hypertension.CEN Case Rep. 2017 May;6(1):66-73. doi: 10.1007/s13730-016-0246-x. Epub 2017 Jan 16. CEN Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28509129 Free PMC article.
-
Antifibrotic Roles of RAAS Blockers: Update.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1165:671-691. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-8871-2_33. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31399990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Should ACE inhibitors and ARBs be used in combination in children?Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Sep;34(9):1521-1532. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-4046-8. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30112656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Remuzzi G, Perico N, Macia M, Ruggenenti P. The role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the progression of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2005;99:S57–S65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

