The association of albumin/creatinine ratio with postoperative AKI in children undergoing cardiac surgery
- PMID: 22917706
- PMCID: PMC3488954
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.12751211
The association of albumin/creatinine ratio with postoperative AKI in children undergoing cardiac surgery
Abstract
Background and objectives: This study determined if preoperative and postoperative urine albumin/creatinine ratios (ACRs) predict postoperative AKI in children undergoing cardiac surgery (CS).
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: This was a three-center, prospective study (2007-2009) of 294 children undergoing CS (n=145 aged <2 years). Urine ACR was measured preoperatively and 0-6 hours after intensive care unit arrival. AKI outcomes were based on the Acute Kidney Injury Network serum creatinine (SCr) criteria (stage 1 AKI, ≥50% or 0.3 mg/dl SCr rise from baseline; and stage 2 or worse AKI, ≥SCr doubling or dialysis). AKI was predicted using preoperative and postoperative ACRs and postoperative ACR performance was compared with other AKI biomarkers.
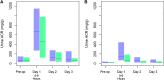
Results: Preoperative ACR did not predict AKI in younger or older children. In children aged <2 years, first postoperative ACR ≥908 mg/g (103 mg/mmol) predicted stage 2 AKI development (adjusted relative risk, 3.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.2-9.4). In children aged ≥2 years, postoperative ACR ≥169 mg/g (19.1 mg/mmol) predicted stage 1 AKI (adjusted relative risk, 2.1; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-4.1). In children aged ≥2 years, first postoperative ACR improved AKI prediction from other biomarker and clinical prediction models, estimated by net reclassification improvement (P≤0.03), but only when serum cystatin C was also included in the model.
Conclusions: Postoperative ACR is a readily available early diagnostic test for AKI after pediatric CS that performs similarly to other AKI biomarkers; however, its use is enhanced in children aged ≥2 years and in combination with serum cystatin C.
Figures
Comment in
-
We can diagnose AKI "early".Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Nov;7(11):1741-2. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09740912. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 23065498 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zappitelli M, Bernier PL, Saczkowski RS, Tchervenkov CI, Gottesman R, Dancea A, Hyder A, Alkandari O: A small post-operative rise in serum creatinine predicts acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 76: 885–892, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL: Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 71: 1028–1035, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Alkandari O, Eddington KA, Hyder A, Gauvin F, Ducruet T, Gottesman R, Phan V, Zappitelli M: Acute kidney injury is an independent risk factor for pediatric intensive care unit mortality, longer length of stay and prolonged mechanical ventilation in critically ill children: A two-center retrospective cohort study. Crit Care 15: R146, 2011 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schneider J, Khemani R, Grushkin C, Bart R: Serum creatinine as stratified in the RIFLE score for acute kidney injury is associated with mortality and length of stay for children in the pediatric intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 38: 933–939, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

