Twenty-four-hour effects of bimatoprost 0.01% monotherapy on intraocular pressure and ocular perfusion pressure
- PMID: 22918671
- PMCID: PMC3951976
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001106
Twenty-four-hour effects of bimatoprost 0.01% monotherapy on intraocular pressure and ocular perfusion pressure
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the 24 h effects of bimatoprost 0.01% monotherapy on intraocular pressure (IOP) and ocular perfusion pressure (OPP).
Design: Prospective, open-label experimental study.
Setting: Single tertiary ophthalmic clinic.
Participants: Sixteen patients with diagnosed primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) or ocular hypertension (ages, 49-77 years).
Interventions: Baseline data of 24 h IOP in untreated patients were collected in a sleep laboratory. Measurements of IOP were taken using a pneumatonometer every 2 h in the sitting and supine body positions during the 16 h diurnal/wake period and in the supine position during the 8 h nocturnal/sleep period. After baseline measurements were taken, patients were treated with bimatoprost 0.01% one time per day at bedtime for 4 weeks, and then 24 h IOP data were collected under the same laboratory conditions.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Diurnal and nocturnal IOP and OPP means under bimatoprost 0.01% treatment were compared with baseline.
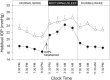
Results: The diurnal and nocturnal IOP means were significantly lower under the bimatoprost 0.01% treatment than baseline in both the sitting and supine positions. The diurnal and nocturnal OPP means were significantly higher under treatment than baseline in both the sitting and supine positions.
Conclusion: Bimatoprost 0.01% monotherapy significantly lowered IOP and increased OPP during the 24 h period.
Figures

References
-
- Weinreb RN, Khaw PT. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Lancet 2004;363:1711–20 - PubMed
-
- Weinreb RN, Harris A. Ocular blood flow in Glaucoma. WGA consensus series 6. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Kugler Publications, 2009:59–128
-
- Medeiros FA, Brandt J, Liu J, et al. IOP as a risk factor for glaucoma development and progression. In: Weinreb RN, Brandt JD, Garway-Heath DF, et al. Intraocular pressure: reports and consensus statements of the 4th Global AIGS Consensus meeting on intraocular pressure. The Hague, The Netherlands: Kugler, 2007:59–74 WGA Consensus Series 4
-
- Bagga H, Liu JH, Weinreb RN. Intraocular pressure measurements throughout the 24 h. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2009;20:79–83 - PubMed
-
- Orzalesi N, Rossetti L, Invernizzi T, et al. Effect of timolol, latanoprost, and dorzolamide on circadian IOP in glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2000;41:2566–73 - PubMed
