Nucleolar accumulation of APE1 depends on charged lysine residues that undergo acetylation upon genotoxic stress and modulate its BER activity in cells
- PMID: 22918947
- PMCID: PMC3469522
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-04-0299
Nucleolar accumulation of APE1 depends on charged lysine residues that undergo acetylation upon genotoxic stress and modulate its BER activity in cells
Abstract
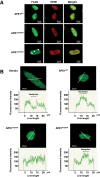
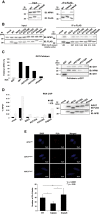
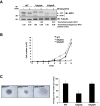
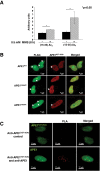
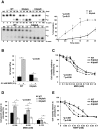
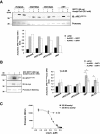
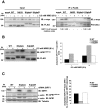
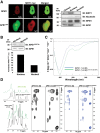
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) is the main abasic endonuclease in the base excision repair (BER) pathway of DNA lesions caused by oxidation/alkylation in mammalian cells; within nucleoli it interacts with nucleophosmin and rRNA through N-terminal Lys residues, some of which (K(27)/K(31)/K(32)/K(35)) may undergo acetylation in vivo. Here we study the functional role of these modifications during genotoxic damage and their in vivo relevance. We demonstrate that cells expressing a specific K-to-A multiple mutant are APE1 nucleolar deficient and are more resistant to genotoxic treatment than those expressing the wild type, although they show impaired proliferation. Of interest, we find that genotoxic treatment induces acetylation at these K residues. We also find that the charged status of K(27)/K(31)/K(32)/K(35) modulates acetylation at K(6)/K(7) residues that are known to be involved in the coordination of BER activity through a mechanism regulated by the sirtuin 1 deacetylase. Of note, structural studies show that acetylation at K(27)/K(31)/K(32)/K(35) may account for local conformational changes on APE1 protein structure. These results highlight the emerging role of acetylation of critical Lys residues in regulating APE1 functions. They also suggest the existence of cross-talk between different Lys residues of APE1 occurring upon genotoxic damage, which may modulate APE1 subnuclear distribution and enzymatic activity in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Arena S, Renzone G, Novi G, Paffetti A, Bernardini G, Santucci A, Scaloni A. Modern proteomic methodologies for the characterization of lactosylation protein targets in milk. Proteomics. 2010;10:3414–3434. - PubMed
-
- Bartels C, Xia T, Billeter M, Gunthert P, Wüthrich K. The program XEASY for computer-supported NMR spectral analysis of biological macromolecules. J Biomol NMR. 1995;6:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

