Mechanisms of post-intervention arterial remodelling
- PMID: 22918976
- PMCID: PMC3500049
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvs276
Mechanisms of post-intervention arterial remodelling
Abstract
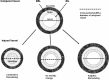
It has been appreciated over the past two decades that arterial remodelling, in addition to intimal hyperplasia, contributes significantly to the degree of restenosis that develops following revascularization procedures. Remodelling appears to be an adventitia-based process that is contributed to by multiple factors including cytokines and growth factors that regulate extracellular matrix or phenotypic transformation of vascular cells including myofibroblasts. In this review, we summarize the currently available information from animal models as well as clinical investigations regarding arterial remodelling. The factors that contribute to this process are presented with an emphasis on potential therapeutic methods to enhance favourable remodelling and prevent restenosis.
Figures

References
-
- Schillinger M, Exner M, Minar E, Mlekusch W, Mullner M, Mannhalter C, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 genotype and restenosis after balloon angioplasty: a novel vascular protective factor. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:950–957. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.09.058. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khan R, Agrotis A, Bobik A. Understanding the role of transforming growth factor-beta1 in intimal thickening after vascular injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;74:223–234. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.02.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suwanabol PA, Kent KC, Liu B. TGF-beta and restenosis revisited: a Smad link. J Surg Res. 2011;167:287–297. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2010.12.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tsai S, Butler J, Rafii S, Liu B, Kent KC. The role of progenitor cells in the development of intimal hyperplasia. J Vasc Surg. 2009;49:502–510. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2008.07.060. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weintraub WS. The pathophysiology and burden of restenosis. Am J Cardiol. 2007;100:3K–9K. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.06.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

