Cathepsin G induces cell aggregation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells via a 2-step mechanism: catalytic site-independent binding to the cell surface and enzymatic activity-dependent induction of the cell aggregation
- PMID: 22919124
- PMCID: PMC3418687
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/456462
Cathepsin G induces cell aggregation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells via a 2-step mechanism: catalytic site-independent binding to the cell surface and enzymatic activity-dependent induction of the cell aggregation
Abstract
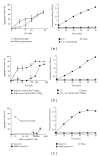
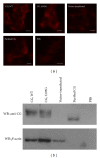
Neutrophils often invade various tumor tissues and affect tumor progression and metastasis. Cathepsin G (CG) is a serine protease secreted from activated neutrophils. Previously, we have shown that CG induces the formation of E-cadherin-mediated multicellular spheroids of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells; however, the molecular mechanisms involved in this process are unknown. In this study, we investigated whether CG required its enzymatic activity to induce MCF-7 cell aggregation. The cell aggregation-inducing activity of CG was inhibited by pretreatment of CG with the serine protease inhibitors chymostatin and phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. In addition, an enzymatically inactive S195G (chymotrypsinogen numbering) CG did not induce cell aggregation. Furthermore, CG specifically bound to the cell surface of MCF-7 cells via a catalytic site-independent mechanism because the binding was not affected by pretreatment of CG with serine protease inhibitors, and cell surface binding was also detected with S195G CG. Therefore, we propose that the CG-induced aggregation of MCF-7 cells occurs via a 2-step process, in which CG binds to the cell surface, independently of its catalytic site, and then induces cell aggregation, which is dependent on its enzymatic activity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neutrophil cathepsin G, but not elastase, induces aggregation of MCF-7 mammary carcinoma cells by a protease activity-dependent cell-oriented mechanism.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:971409. doi: 10.1155/2014/971409. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 24803743 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling is responsible for cathepsin G-induced aggregation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells.Cancer Sci. 2017 Aug;108(8):1574-1583. doi: 10.1111/cas.13286. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28544544 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin G-Induced Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Elevation in MCF-7 Medium Is Caused by Proteolysis of IGF Binding Protein (IGFBP)-2 but Not of IGF-1.Biol Pharm Bull. 2020;43(11):1678-1686. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b20-00389. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020. PMID: 33132312
-
Cathepsin G, a neutrophil protease, induces compact cell-cell adhesion in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.Mediators Inflamm. 2009;2009:850940. doi: 10.1155/2009/850940. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Mediators Inflamm. 2009. PMID: 19920860 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of multicellular 3-D spheroids of MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells by neutrophil-derived cathepsin G and elastase.Cancer Sci. 2005 Sep;96(9):560-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00097.x. Cancer Sci. 2005. PMID: 16128741 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A TP53-based immune prognostic model for muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Dec 15;13(2):1929-1946. doi: 10.18632/aging.202150. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33323544 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-associated macrophages, dendritic cells, and neutrophils: biological roles, crosstalk, and therapeutic relevance.Med Rev (2021). 2022 Feb 14;1(2):222-243. doi: 10.1515/mr-2021-0014. eCollection 2021 Dec. Med Rev (2021). 2022. PMID: 37724296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fenugreek inhibits cathepsin G activity and suppresses the progression of malignant phenotypes in MCF-7 cells.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Apr 21;42:102021. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102021. eCollection 2025 Jun. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40524916 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsins B, D, and G Are Expressed in Metastatic Head and Neck Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 21;11:690460. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.690460. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34621666 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil cathepsin G, but not elastase, induces aggregation of MCF-7 mammary carcinoma cells by a protease activity-dependent cell-oriented mechanism.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:971409. doi: 10.1155/2014/971409. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 24803743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wiedow O, Meyer-Hoffert U. Neutrophil serine proteases: potential key regulators of cell signalling during inflammation. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2005;257(4):319–328. - PubMed
-
- Pham CTN. Neutrophil serine proteases: specific regulators of inflammation. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2006;6(7):541–550. - PubMed
-
- Salvesen G, Farley D, Shuman J, Przybyla A, Reilly C, Travis J. Molecular cloning of human cathepsin G: structural similarity to mast cell and cytotoxic T lymphocyte proteinases. Biochemistry. 1987;26(8):2289–2293. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

